8.4 KiB
Executable File
解题思路:
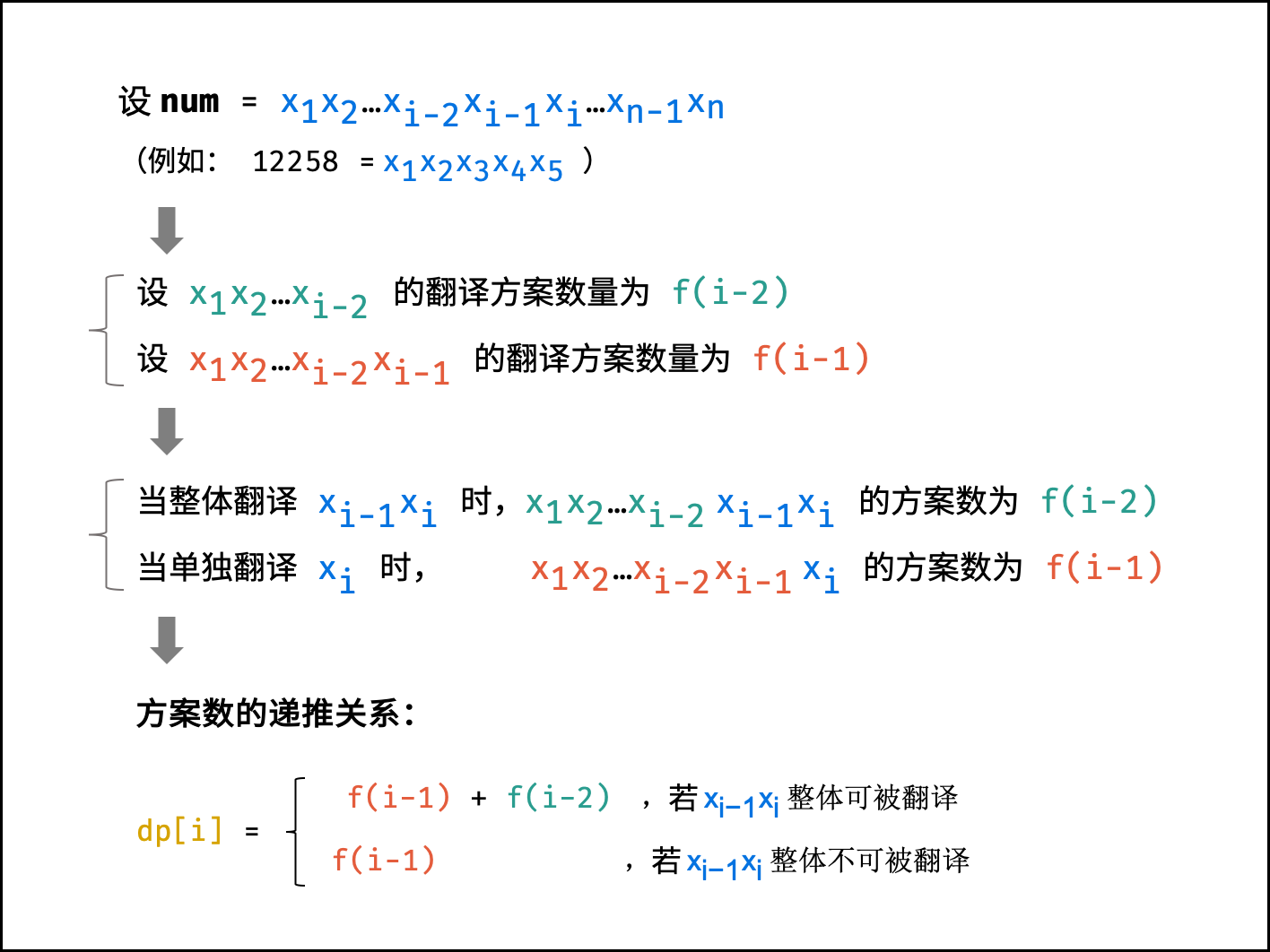
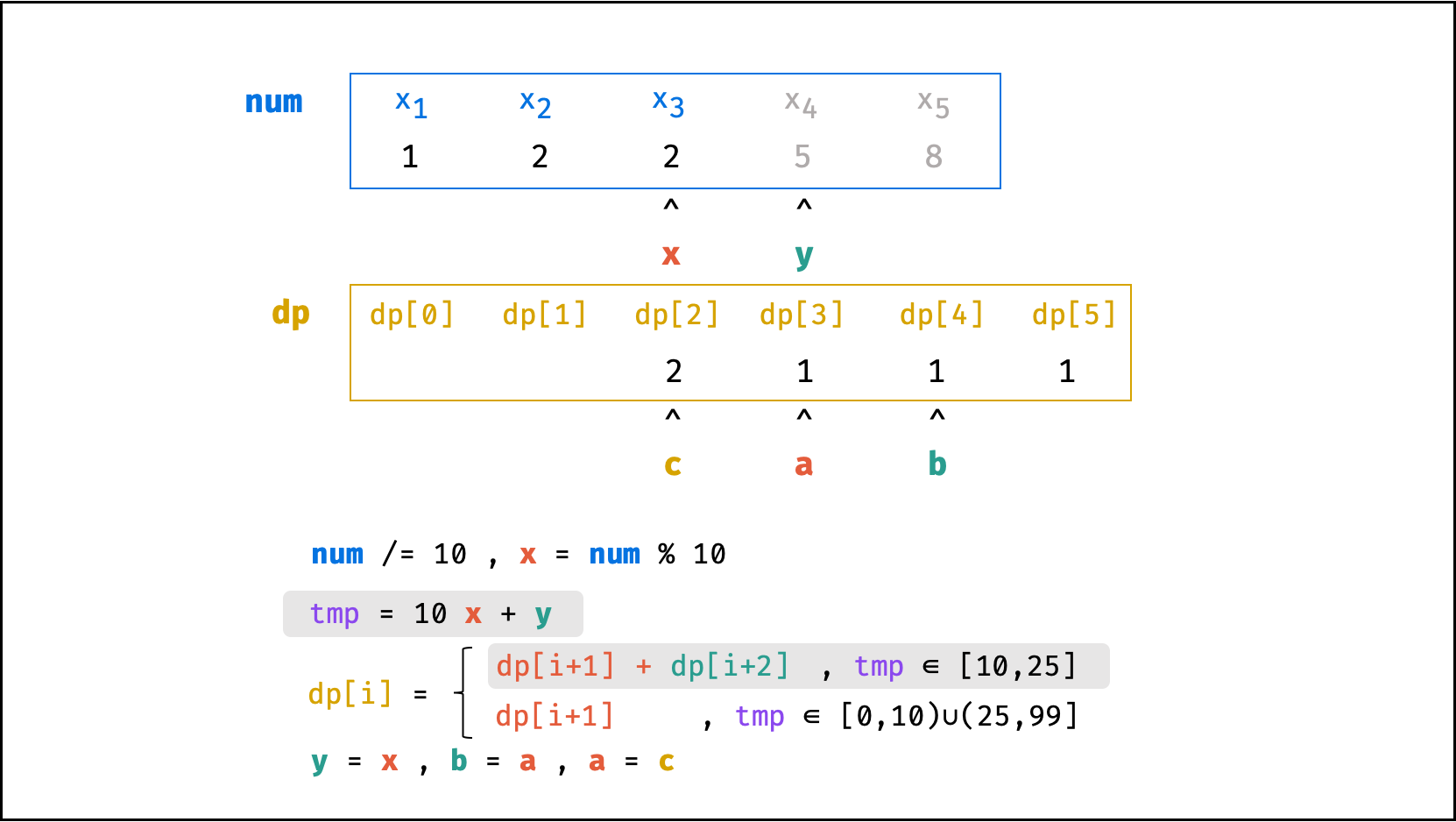
根据题意,可按照下图的思路,总结出 “递推公式” (即转移方程)。
下图中的
num对应本题的ciphertext。
因此,此题可用动态规划解决,以下按照流程解题。
动态规划解析:
记数字
ciphertext第i位数字为x_i,数字ciphertext的位数为n; 例如:ciphertext = 12258的n = 5,x_1 = 1。
-
状态定义: 设动态规划列表
dp,dp[i]代表以x_i为结尾的数字的翻译方案数量。 -
转移方程: 若
x_i和x_{i-1}组成的两位数字可被整体翻译,则dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2],否则dp[i] = dp[i - 1]。
dp[i] =
\begin{cases}
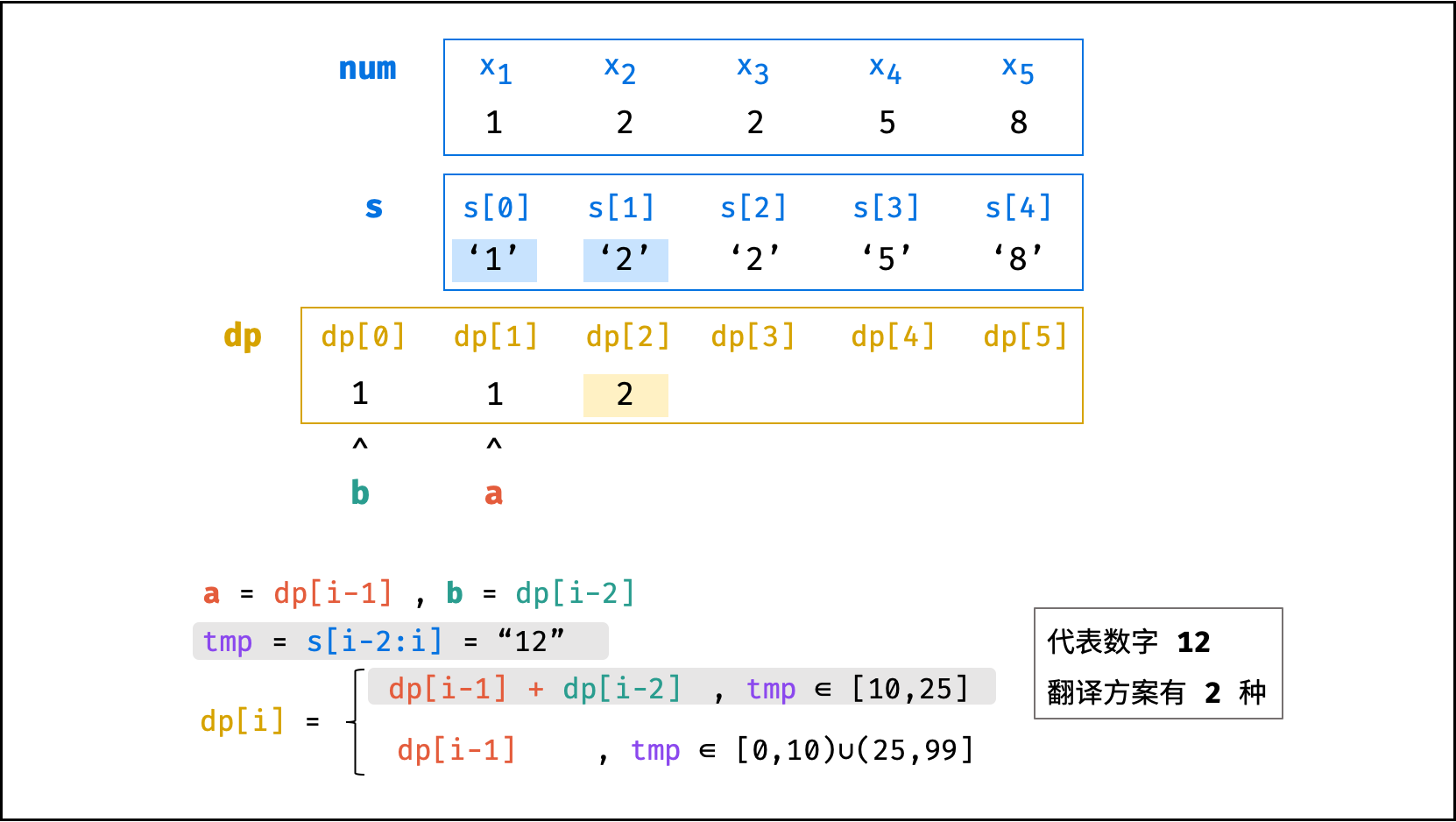
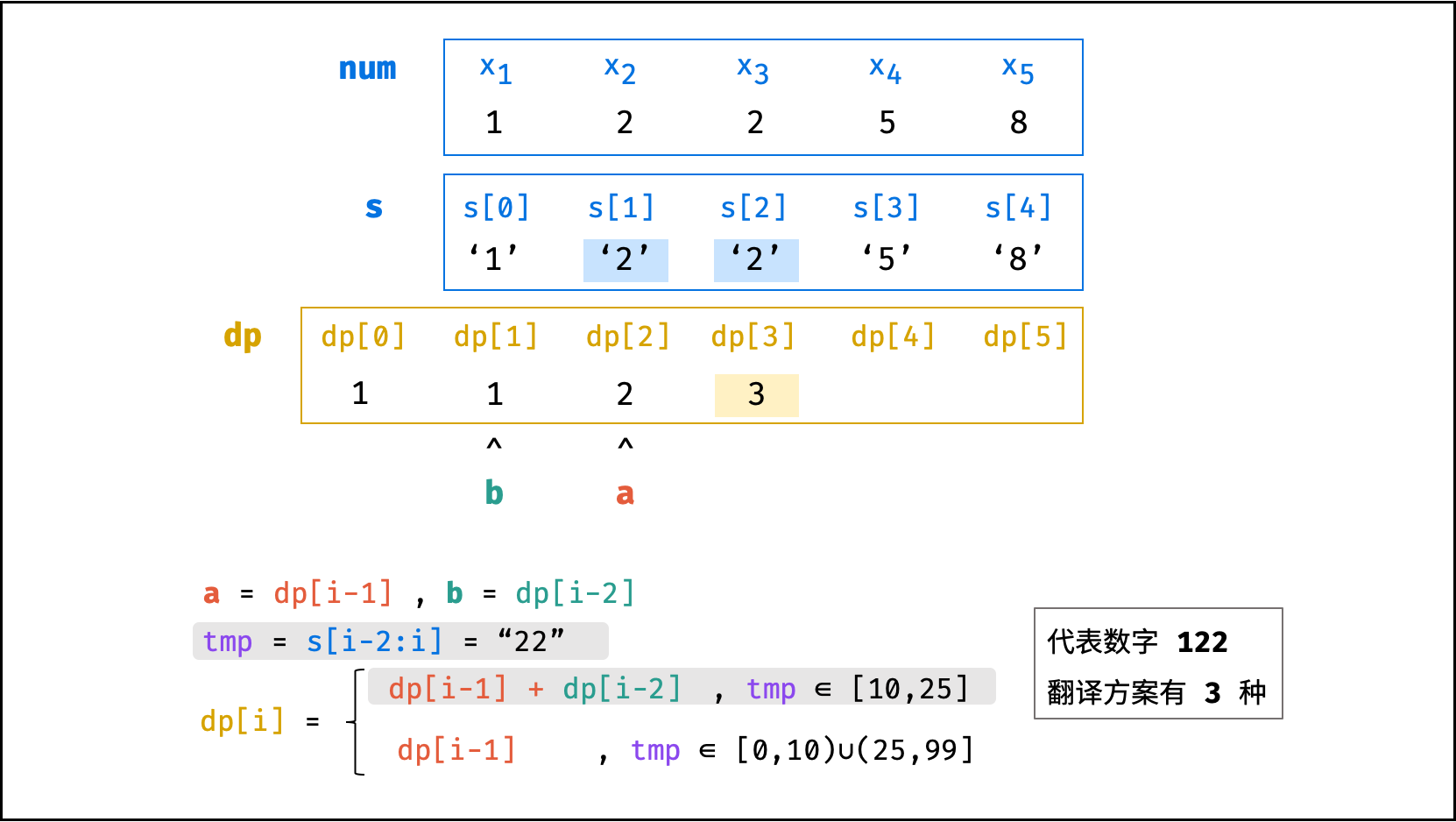
dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2] & {, (10 x_{i-1} + x_i) \in [10,25]} \\
dp[i - 1] & {, (10 x_{i-1} + x_i) \in [0, 10) \cup (25, 99]}
\end{cases}
可被整体翻译的两位数区间分析: 当
x_{i-1} = 0时,组成的两位数无法被整体翻译(例如00, 01, 02, \cdots),大于25的两位数也无法被整体翻译(例如26, 27, \cdots),因此区间为[10, 25]。
-
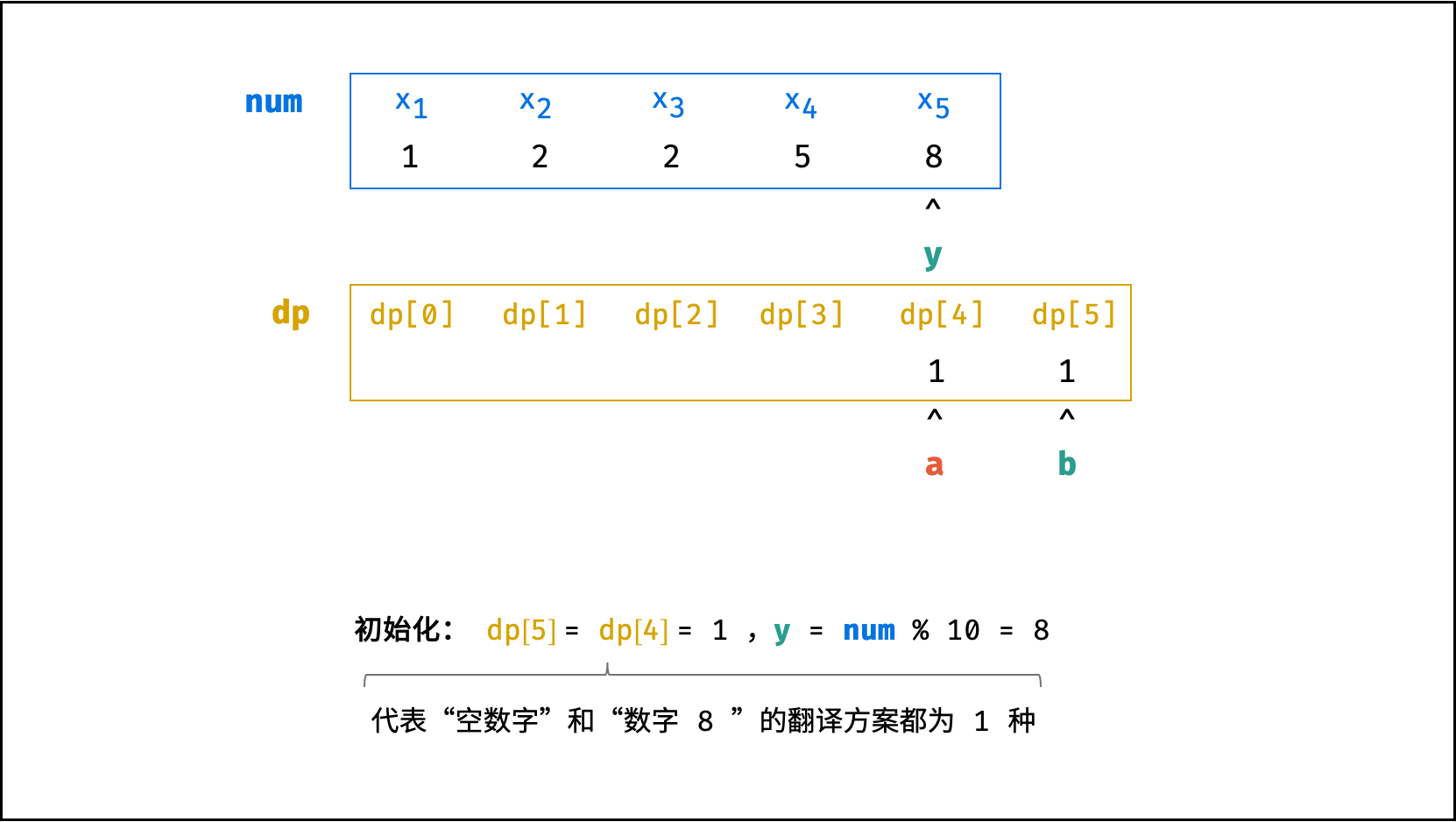
初始状态:
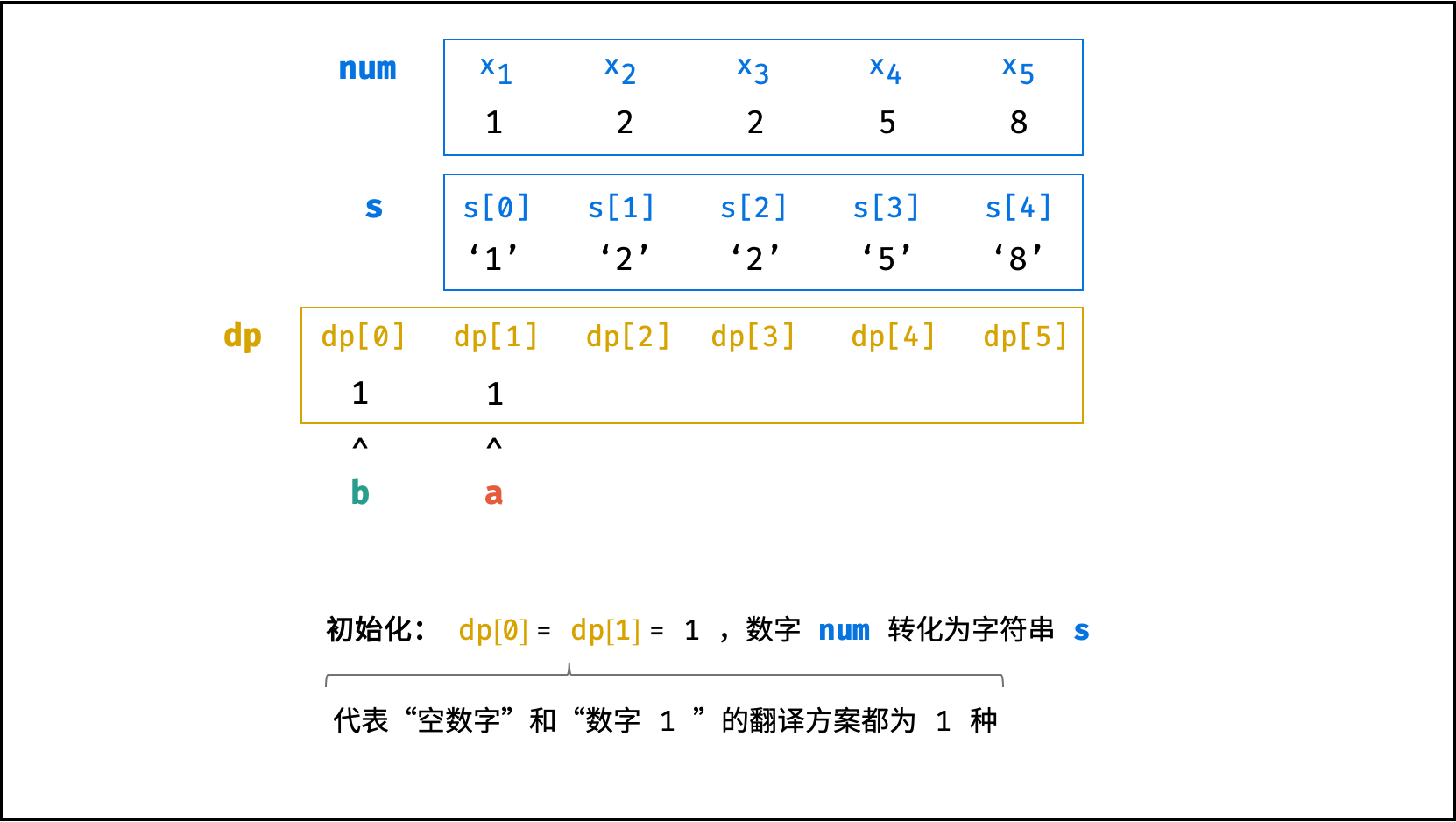
dp[0] = dp[1] = 1,即 “无数字” 和 “第1位数字” 的翻译方法数量均为1; -
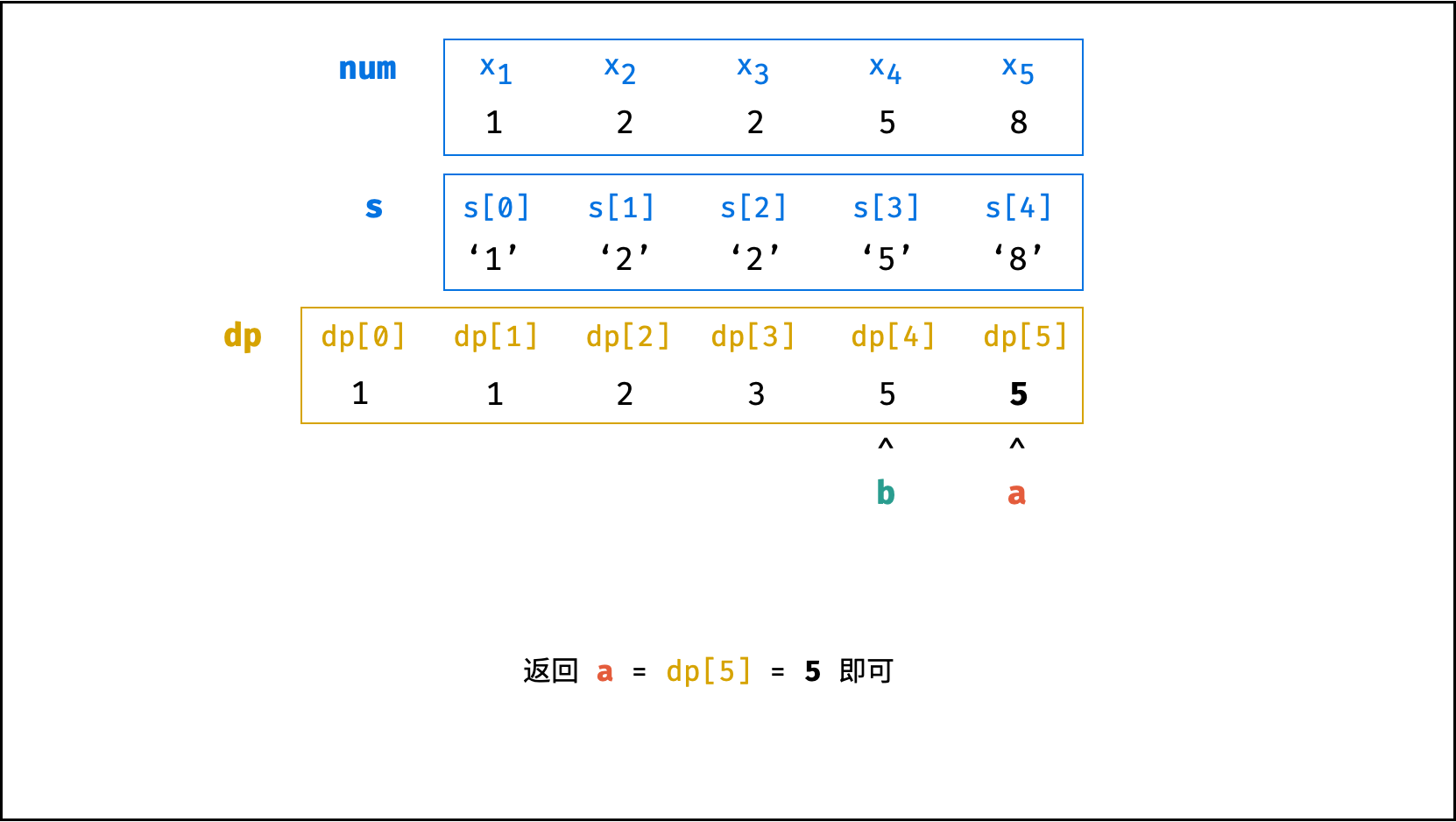
返回值:
dp[n],即此数字的翻译方案数量;
Q: 无数字情况
dp[0] = 1从何而来? A: 当ciphertext第1, 2位的组成的数字\in [10,25]时,显然应有2种翻译方法,即dp[2] = dp[1] + dp[0] = 2,而显然dp[1] = 1,因此推出dp[0] = 1。
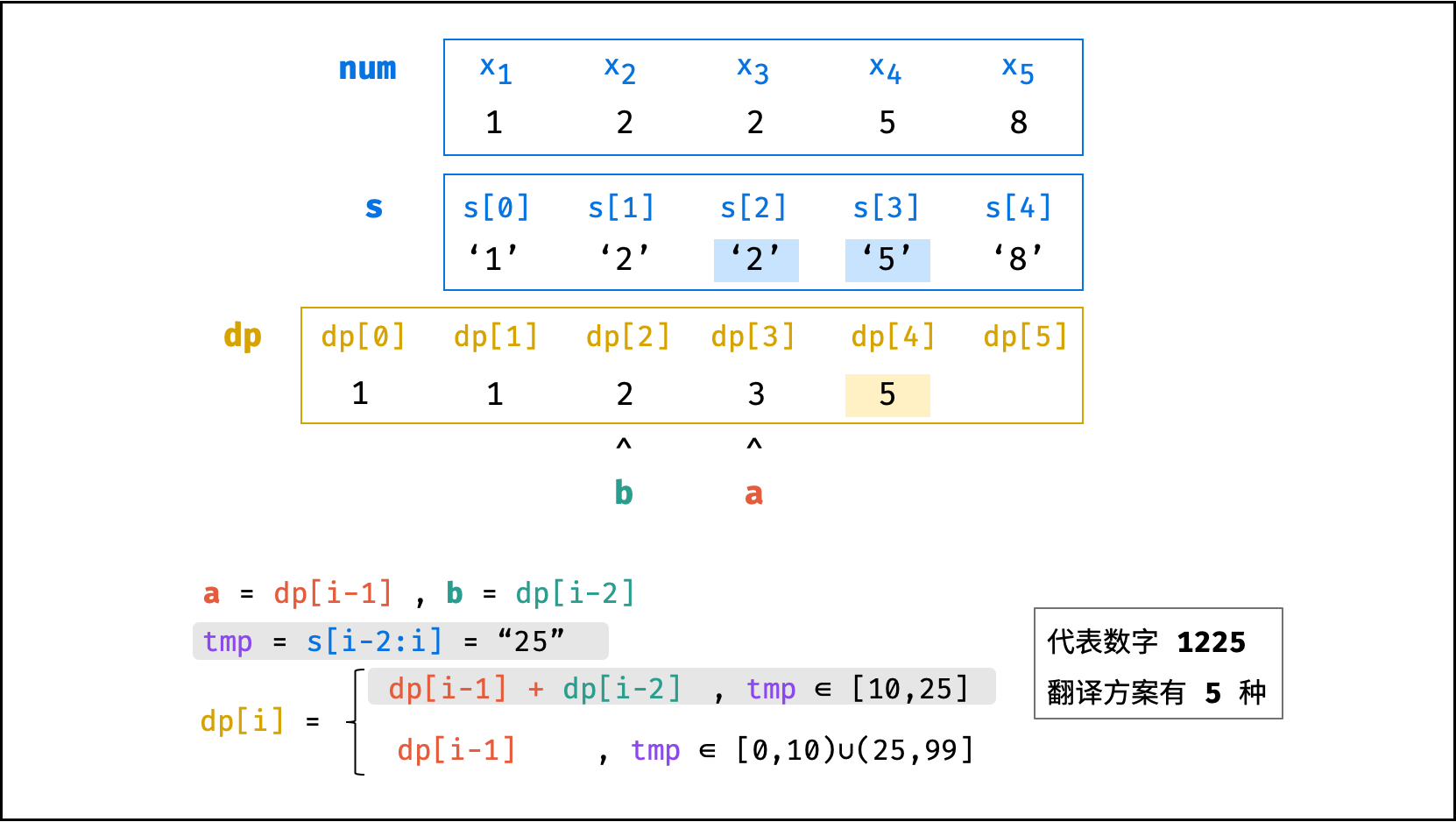
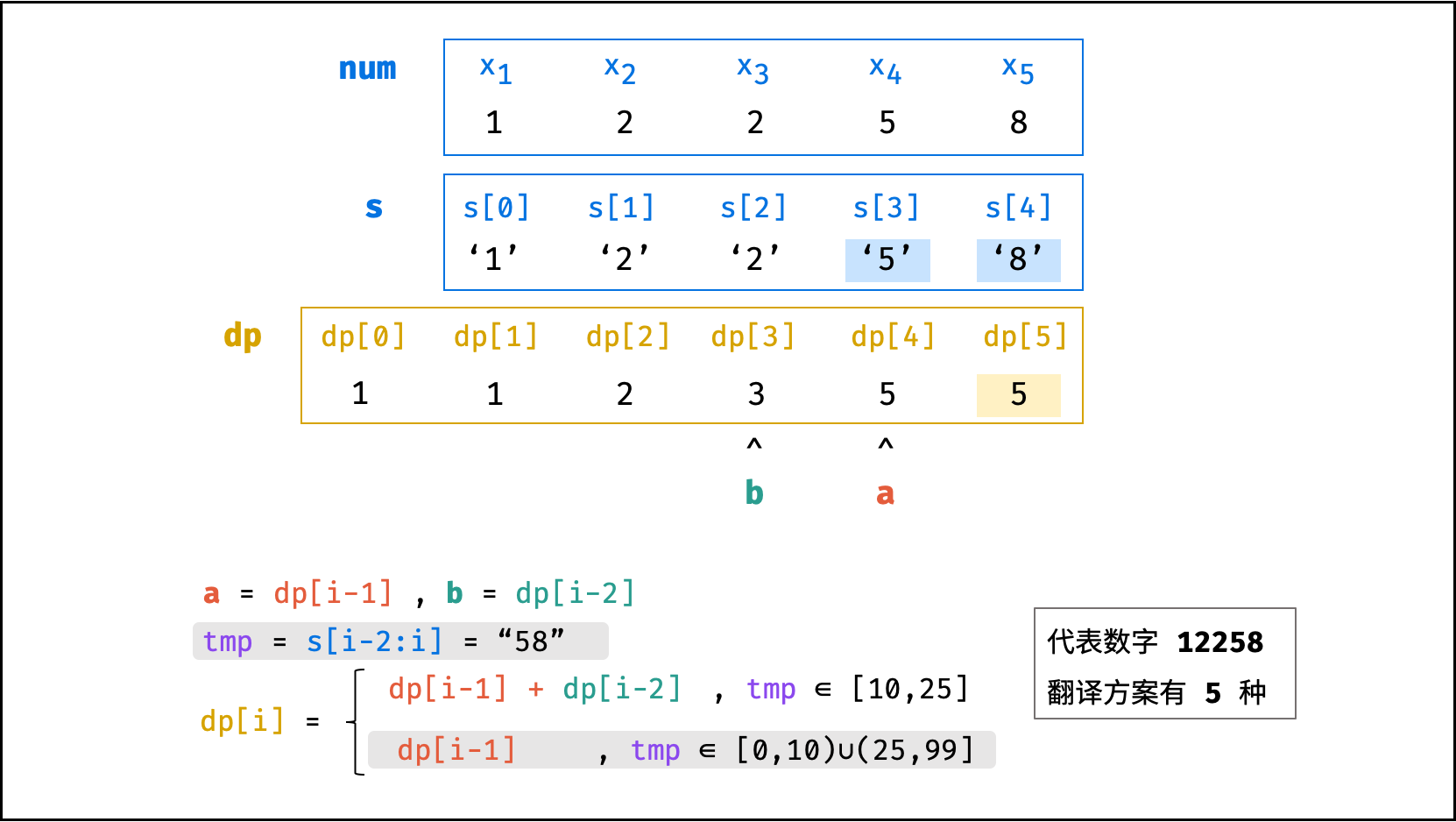
方法一:字符串遍历
- 为方便获取数字的各位
x_i,考虑先将数字ciphertext转化为字符串s,通过遍历s实现动态规划。 - 通过字符串切片
s[i - 2:i]获取数字组合10 x_{i-1} + x_i,通过对比字符串 ASCII 码判断字符串对应的数字区间。 - 空间使用优化: 由于
dp[i]只与dp[i - 1]有关,因此可使用两个变量a, b分别记录dp[i],dp[i - 1],两变量交替前进即可。此方法可省去dp列表使用的O(N)的额外空间。
代码:
class Solution:
def crackNumber(self, ciphertext: int) -> int:
s = str(ciphertext)
a = b = 1
for i in range(2, len(s) + 1):
tmp = s[i - 2:i]
c = a + b if "10" <= tmp <= "25" else a
b = a
a = c
return a
class Solution {
public int crackNumber(int ciphertext) {
String s = String.valueOf(ciphertext);
int a = 1, b = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= s.length(); i++) {
String tmp = s.substring(i - 2, i);
int c = tmp.compareTo("10") >= 0 && tmp.compareTo("25") <= 0 ? a + b : a;
b = a;
a = c;
}
return a;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
int crackNumber(int ciphertext) {
string s = to_string(ciphertext);
int a = 1, b = 1, len = s.size();
for(int i = 2; i <= len; i++) {
string tmp = s.substr(i - 2, 2);
int c = tmp.compare("10") >= 0 && tmp.compare("25") <= 0 ? a + b : a;
b = a;
a = c;
}
return a;
}
};
此题的动态规划计算是 对称的 ,即 从左向右 遍历(从第 dp[2] 计算至 dp[n] )和 从右向左 遍历(从第 dp[n - 2] 计算至 dp[0] )所得方案数一致。从右向左遍历的代码如下所示。
class Solution:
def crackNumber(self, ciphertext: int) -> int:
s = str(ciphertext)
a = b = 1
for i in range(len(s) - 2, -1, -1):
a, b = (a + b if "10" <= s[i:i + 2] <= "25" else a), a
return a
class Solution {
public int crackNumber(int ciphertext) {
String s = String.valueOf(ciphertext);
int a = 1, b = 1;
for(int i = s.length() - 2; i > -1; i--) {
String tmp = s.substring(i, i + 2);
int c = tmp.compareTo("10") >= 0 && tmp.compareTo("25") <= 0 ? a + b : a;
b = a;
a = c;
}
return a;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
int crackNumber(int ciphertext) {
string s = to_string(ciphertext);
int a = 1, b = 1, len = s.size();
for(int i = len - 2; i > -1; i--) {
string tmp = s.substr(i, 2);
int c = tmp.compare("10") >= 0 && tmp.compare("25") <= 0 ? a + b : a;
b = a;
a = c;
}
return a;
}
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度
O(N):N为字符串s的长度(即数字ciphertext的位数\log(ciphertext)),其决定了循环次数。 - 空间复杂度
O(N): 字符串s使用O(N)大小的额外空间。
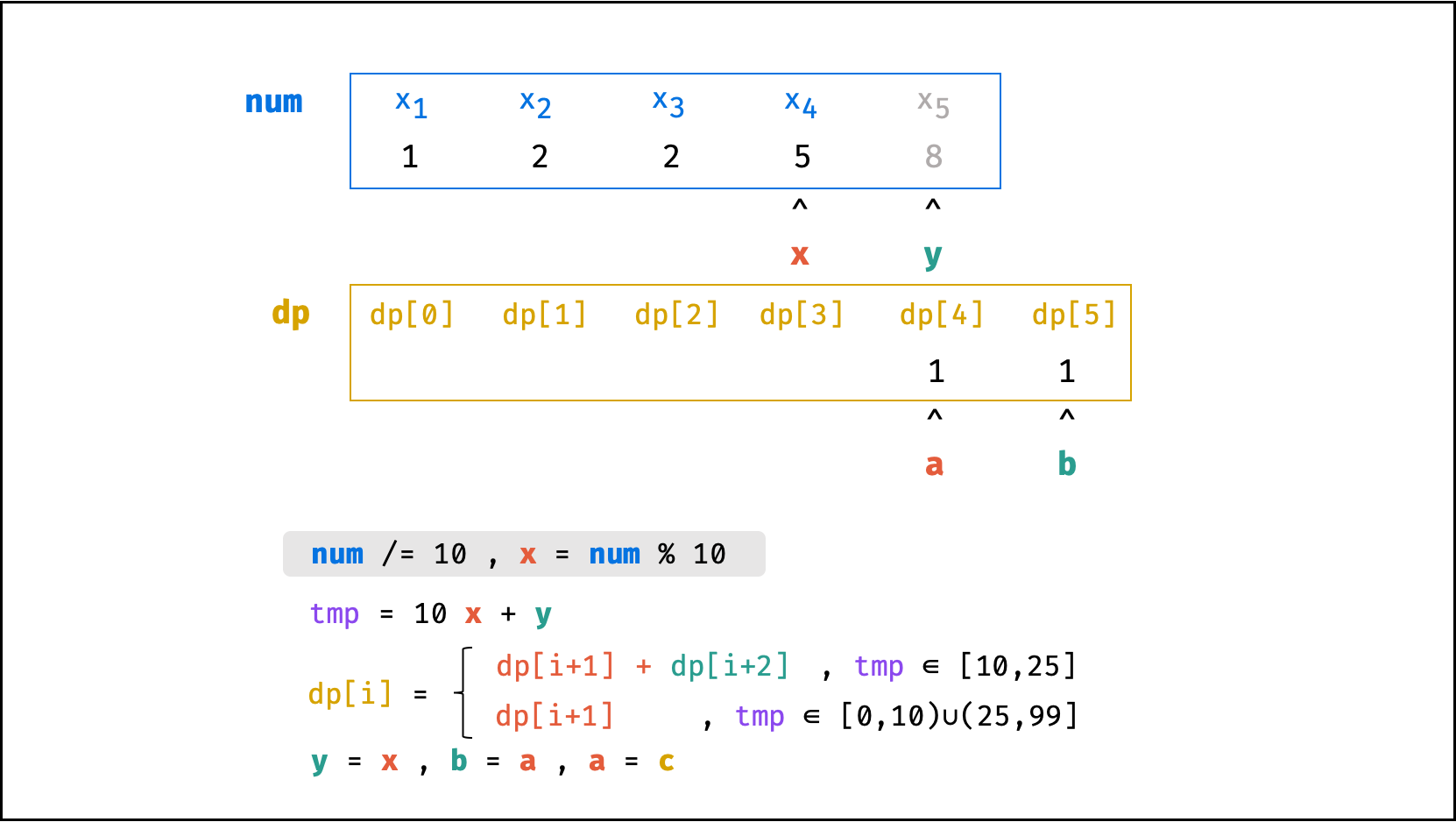
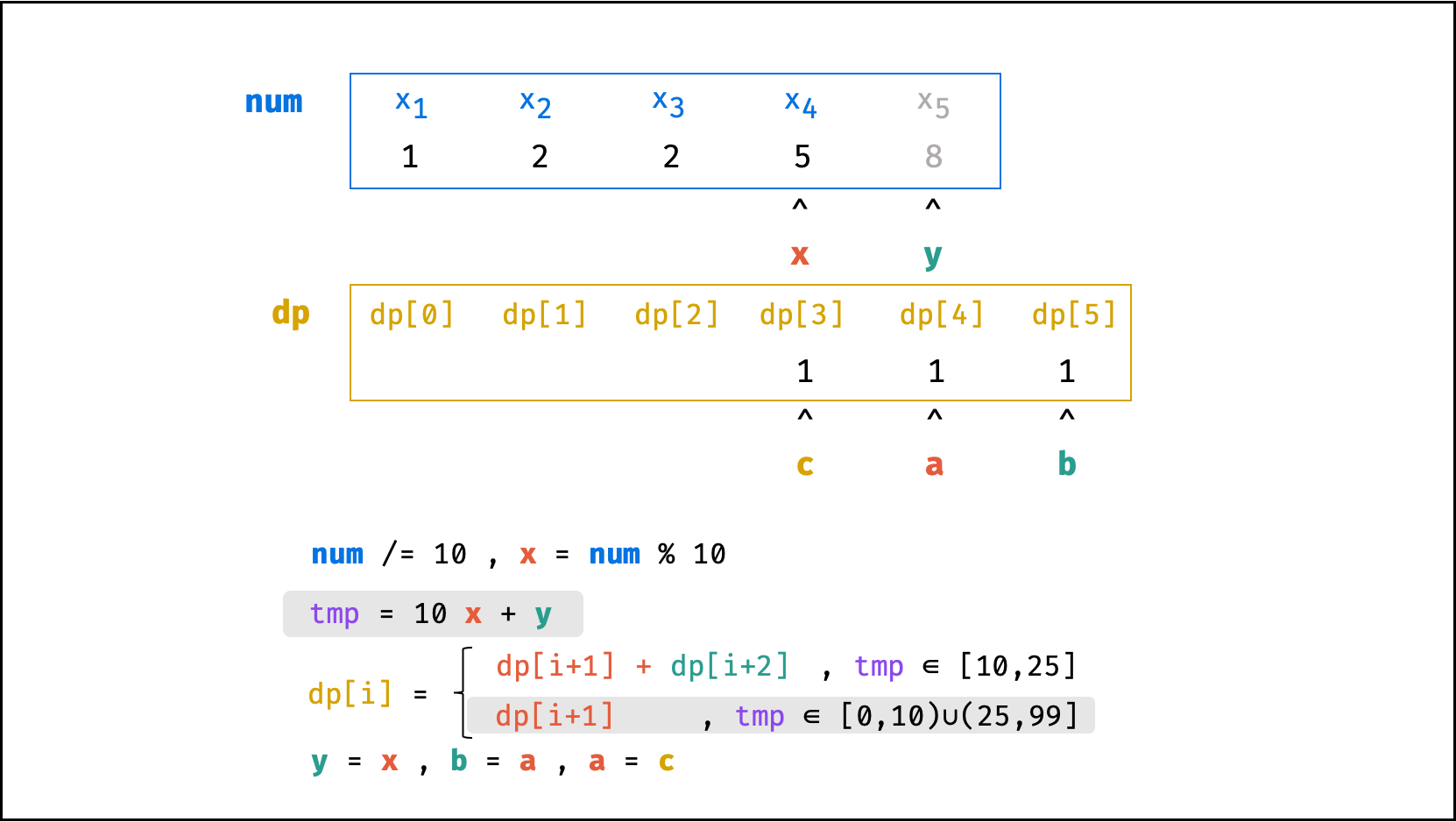
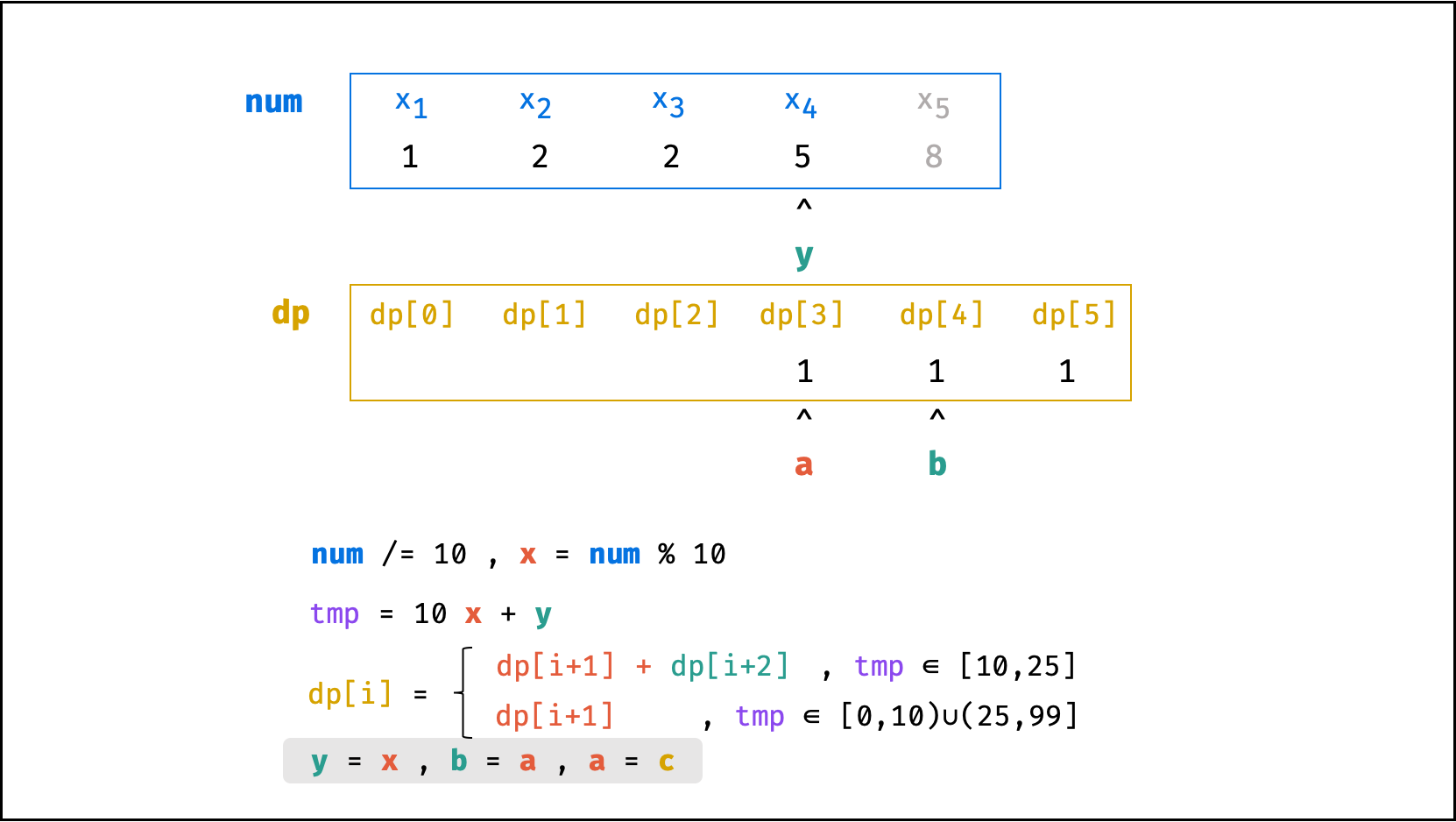
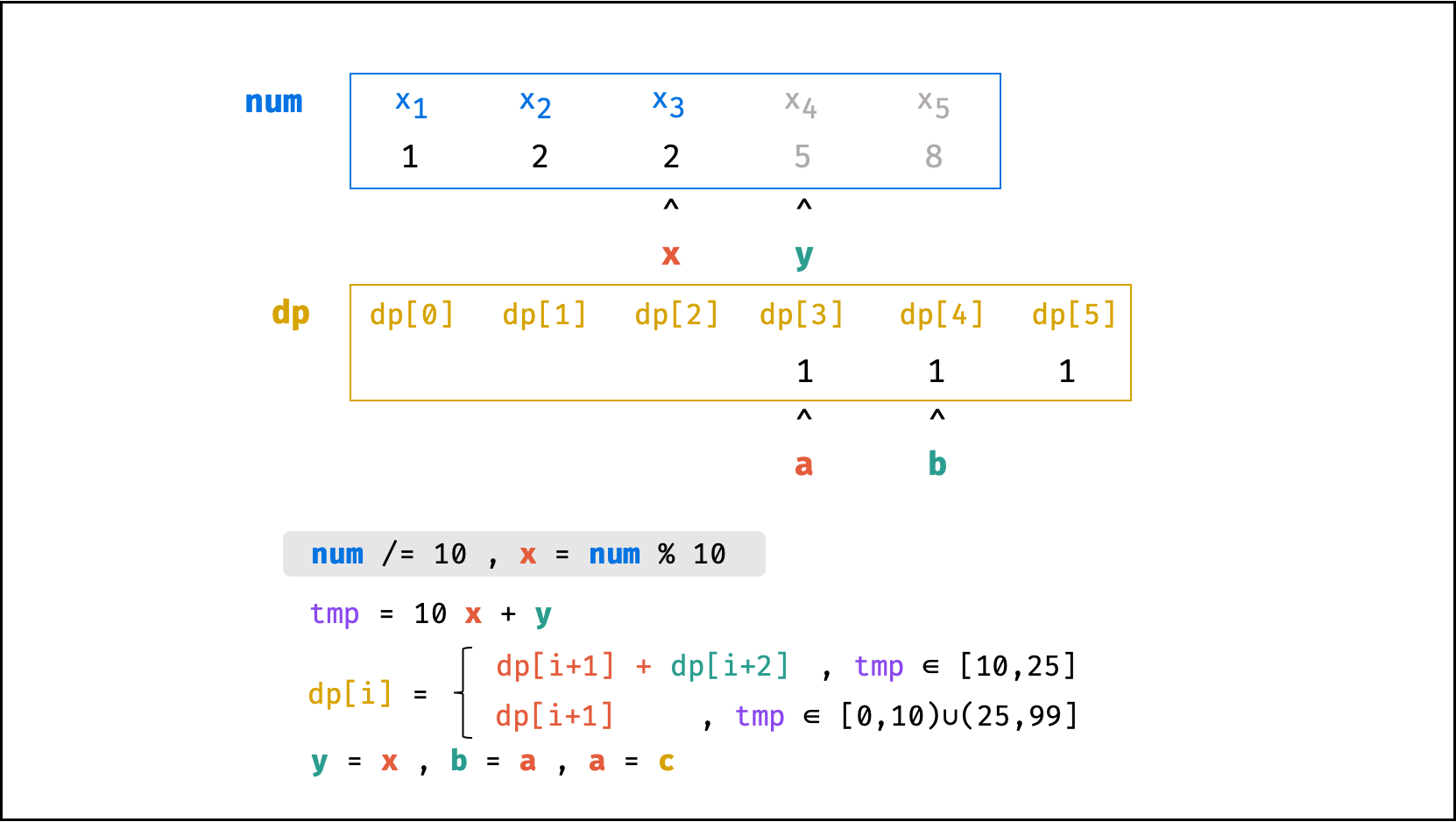
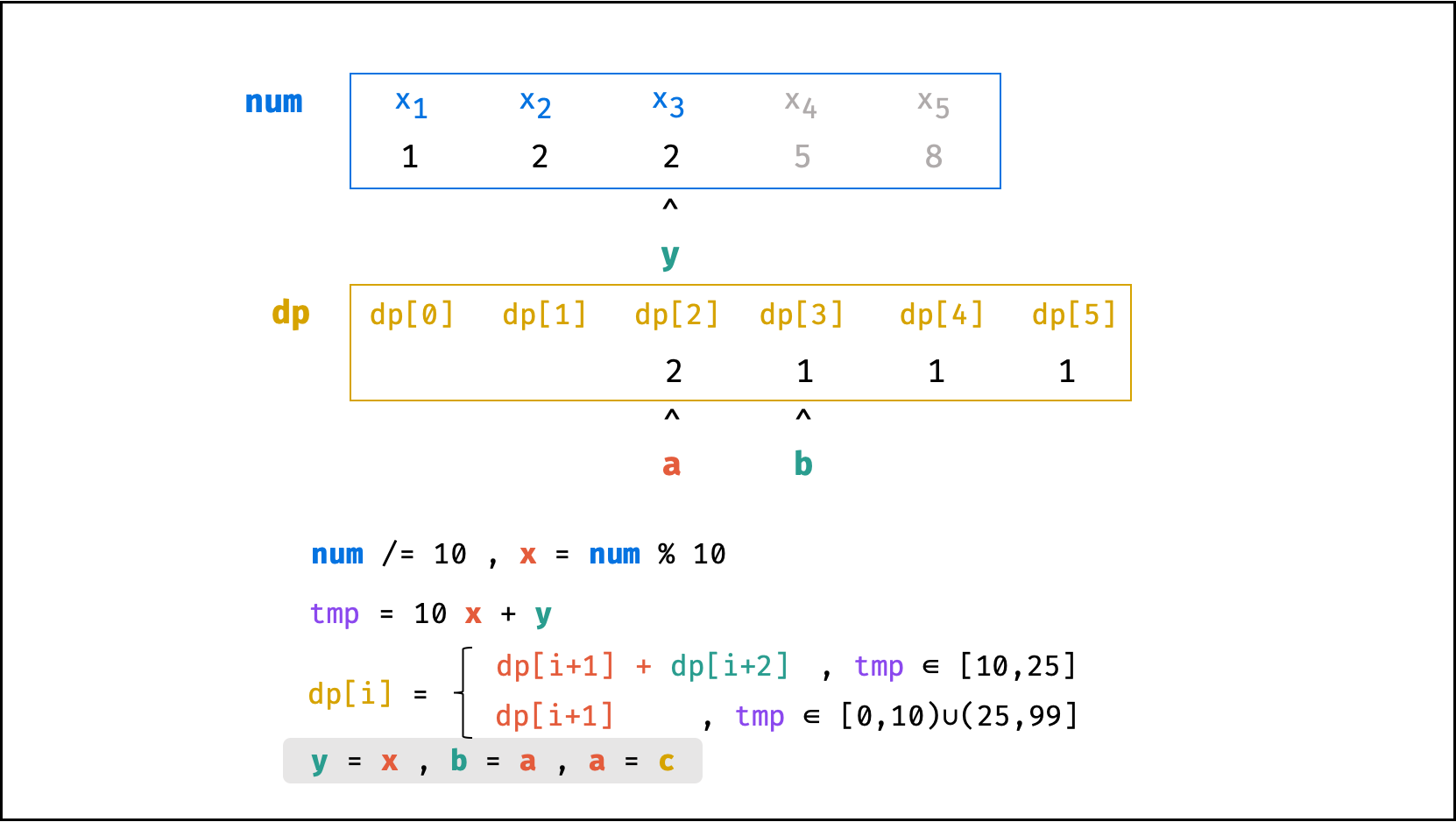
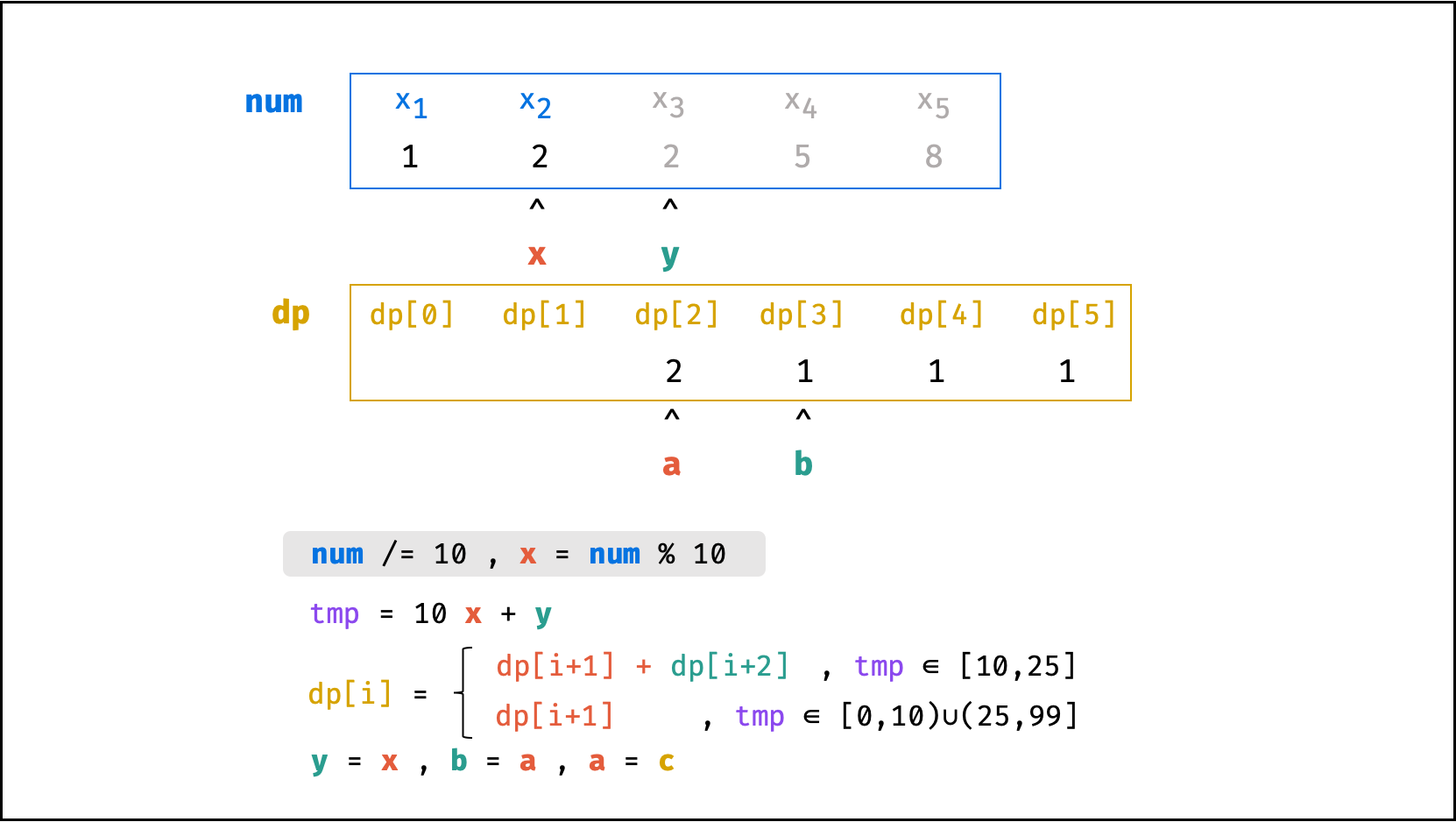
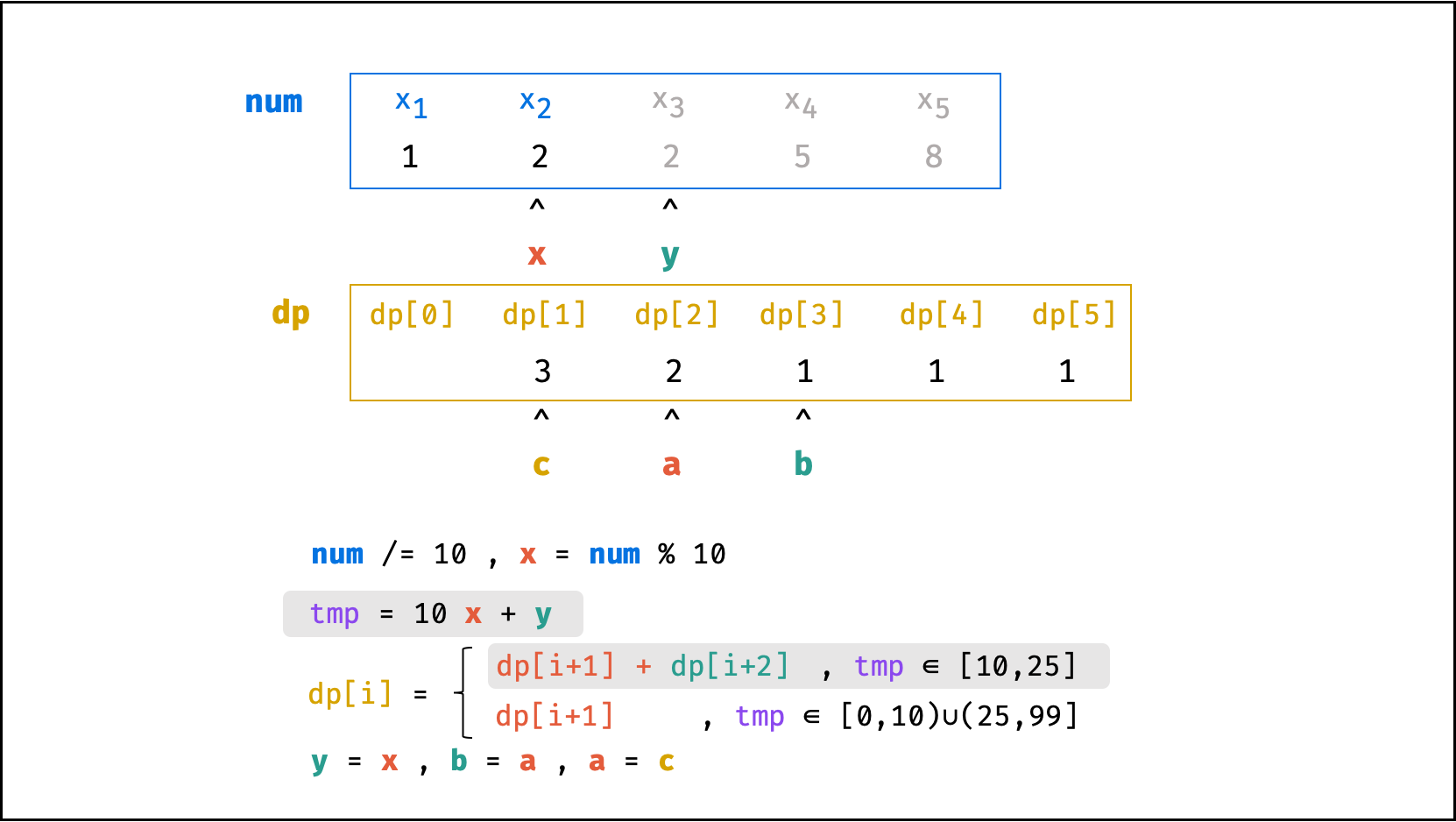
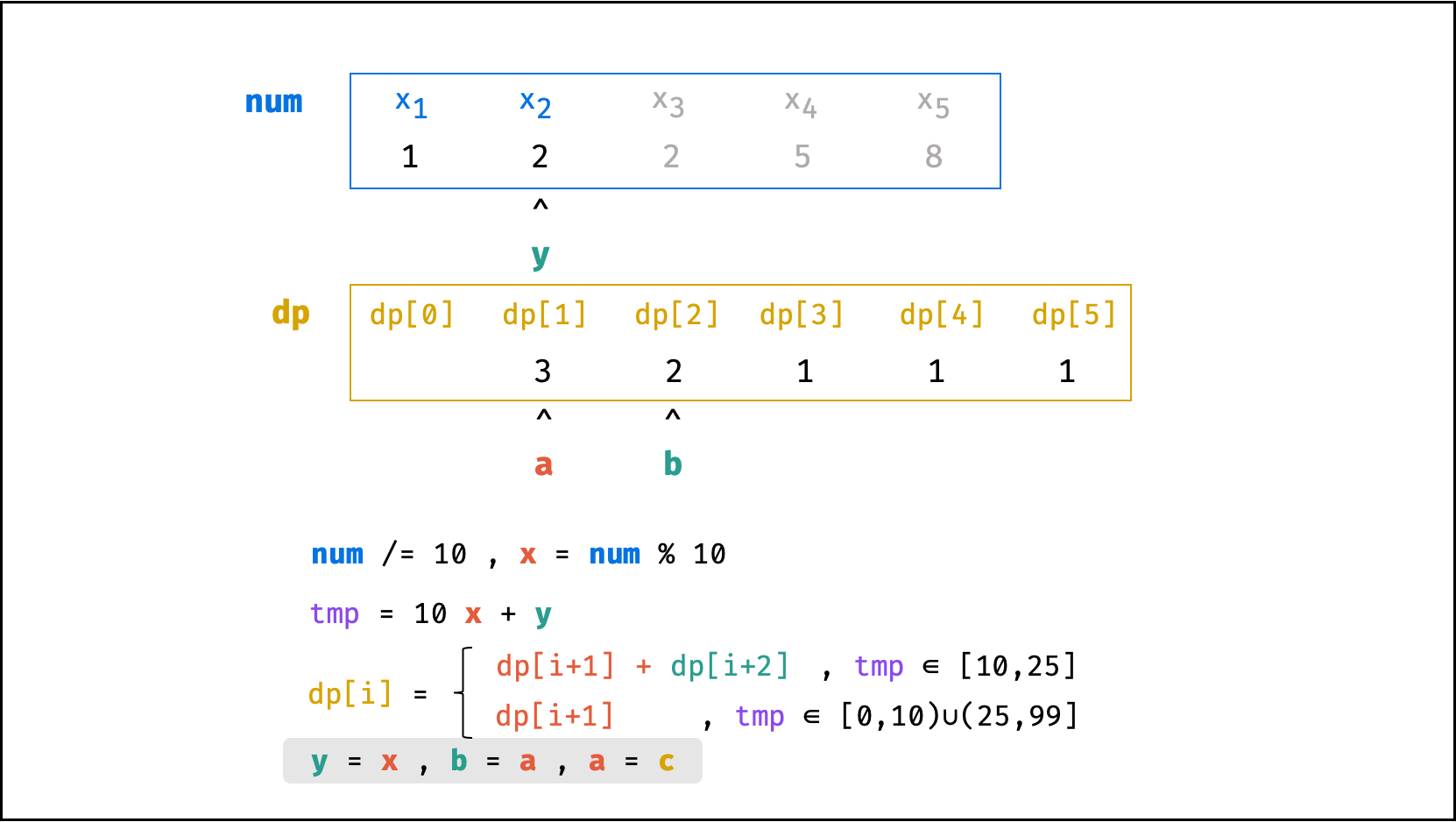
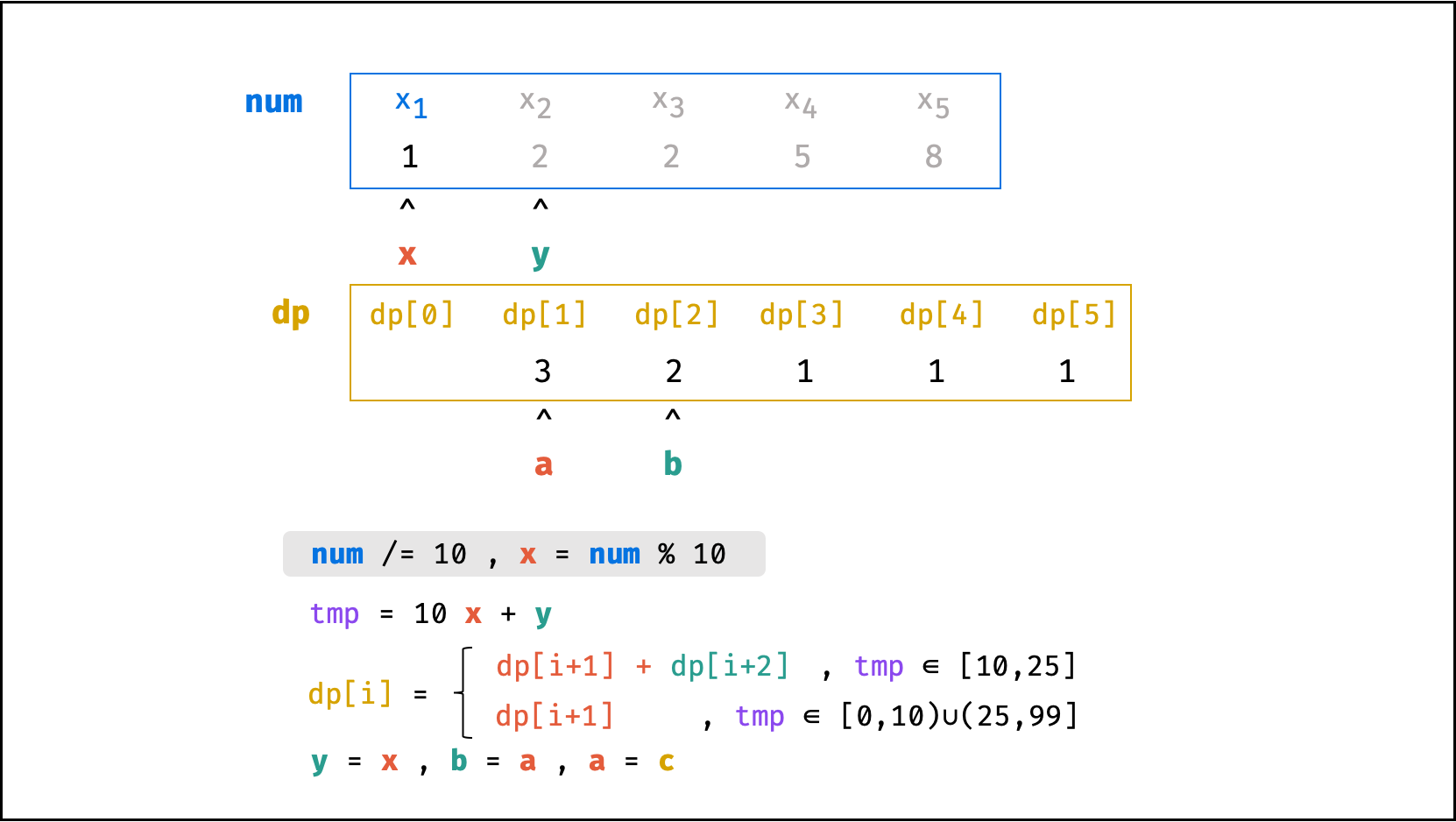
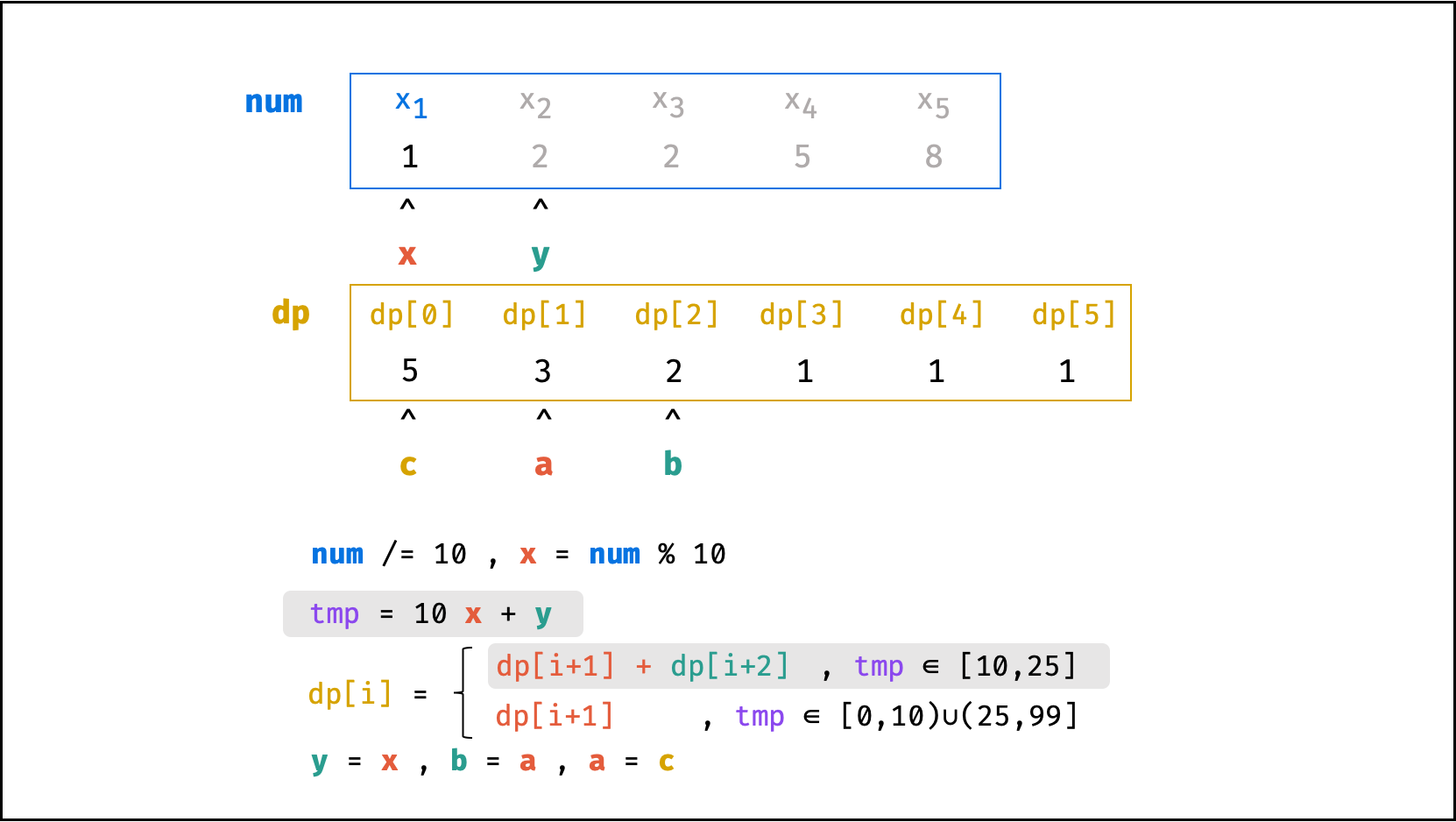
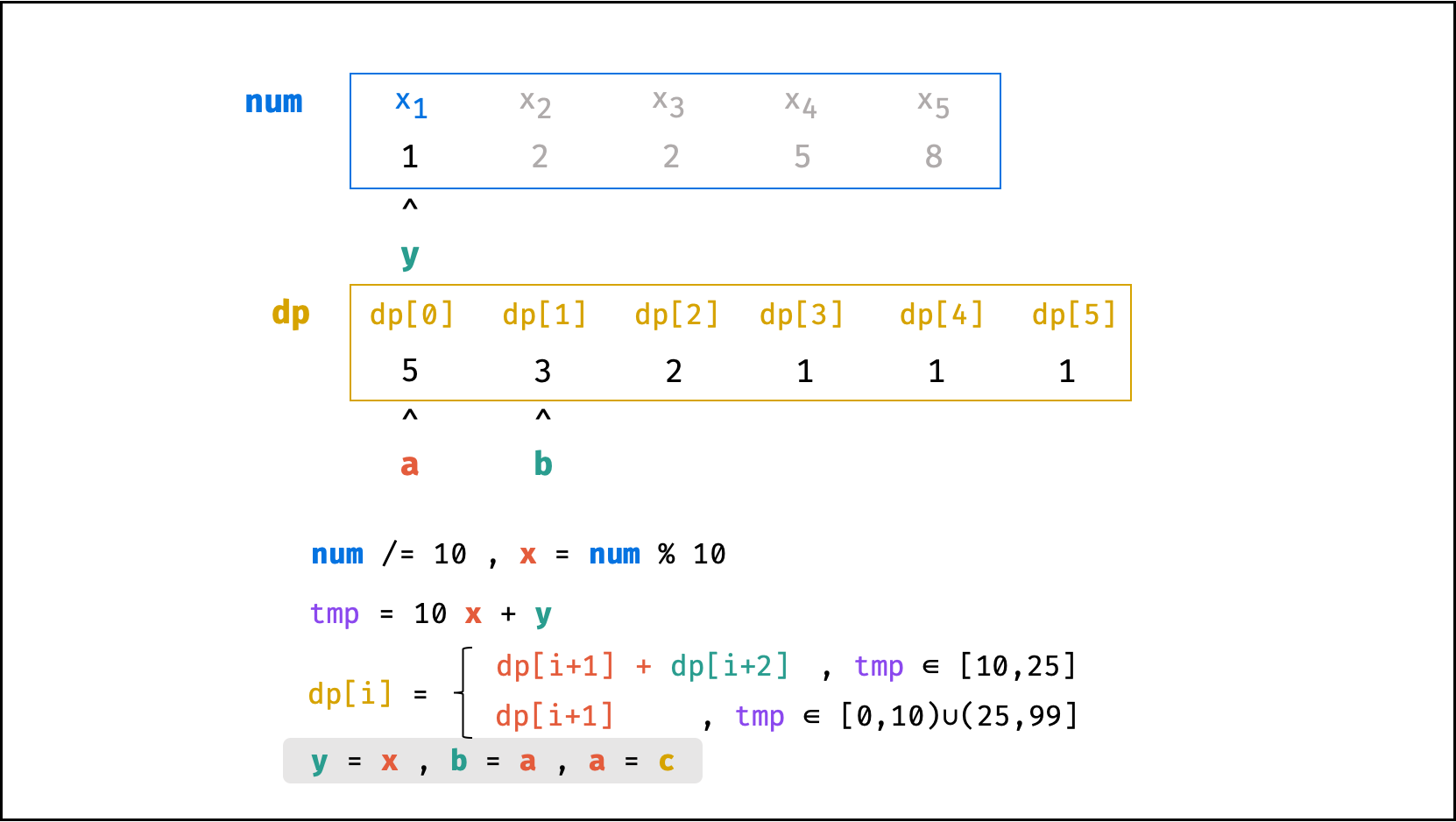
方法二:数字求余
上述方法虽然已经节省了 dp 列表的空间占用,但字符串 s 仍使用了 O(N) 大小的额外空间。
空间优化:
- 利用求余运算
ciphertext \mod 10和求整运算ciphertext // 10,可获取数字ciphertext的各位数字(获取顺序为个位、十位、百位…)。 - 运用 求余 和 求整 运算实现,可实现 从右向左 的动态规划计算。而根据上述动态规划 “对称性” ,可知从右向左计算是正确的。
- 自此,字符串
s的空间占用也被省去,空间复杂度从O(N)降至O(1)。
代码:
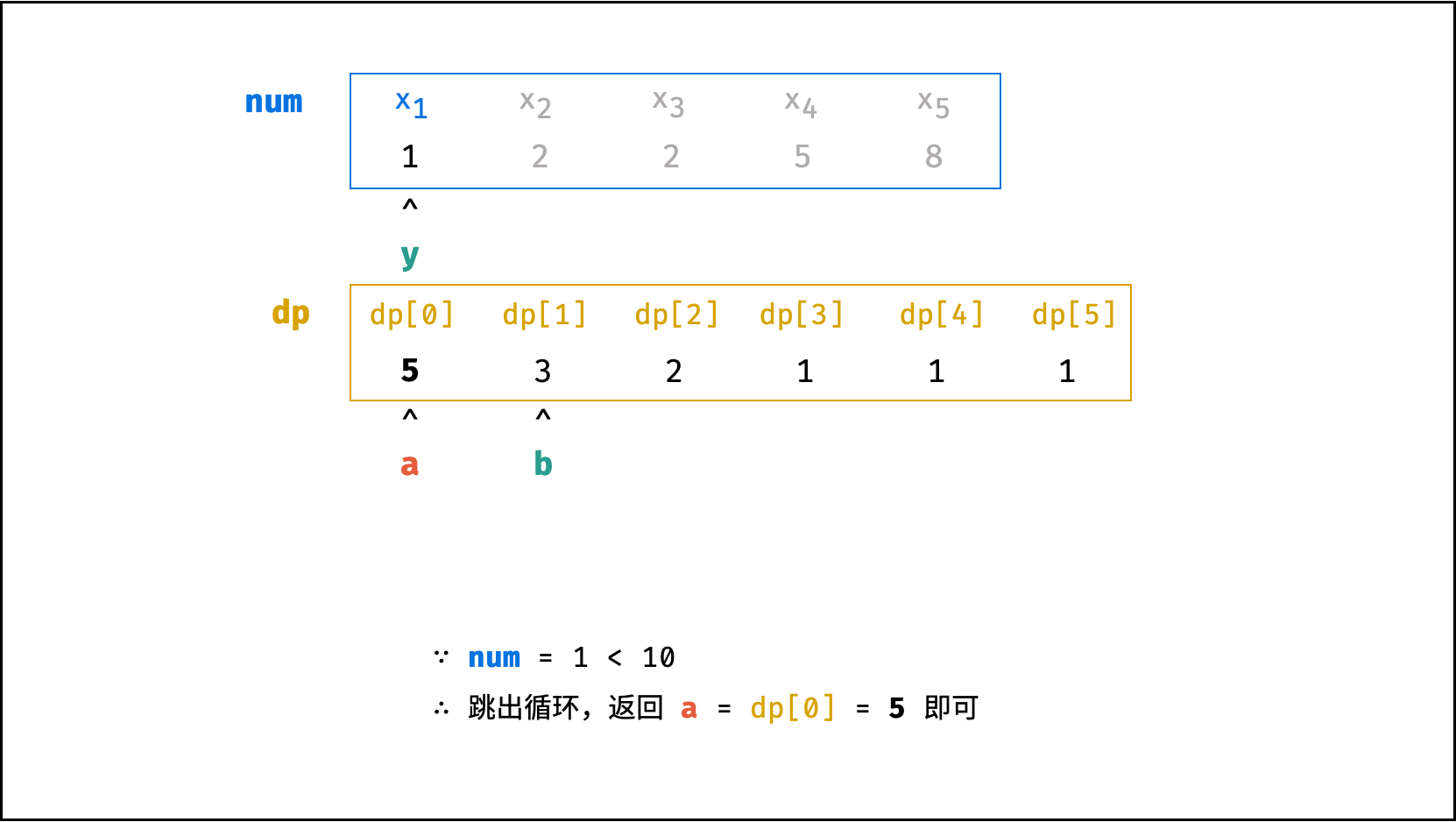
class Solution:
def crackNumber(self, ciphertext: int) -> int:
a = b = 1
y = ciphertext % 10
while ciphertext > 9:
ciphertext //= 10
x = ciphertext % 10
tmp = 10 * x + y
c = a + b if 10 <= tmp <= 25 else a
a, b = c, a
y = x
return a
class Solution {
public int crackNumber(int ciphertext) {
int a = 1, b = 1, x, y = ciphertext % 10;
while(ciphertext > 9) {
ciphertext /= 10;
x = ciphertext % 10;
int tmp = 10 * x + y;
int c = (tmp >= 10 && tmp <= 25) ? a + b : a;
b = a;
a = c;
y = x;
}
return a;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
int crackNumber(int ciphertext) {
int a = 1, b = 1, x, y = ciphertext % 10;
while(ciphertext > 9) {
ciphertext /= 10;
x = ciphertext % 10;
int tmp = 10 * x + y;
int c = (tmp >= 10 && tmp <= 25) ? a + b : a;
b = a;
a = c;
y = x;
}
return a;
}
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度
O(N):N为字符串s的长度,即数字ciphertext的位数\log(ciphertext),其决定了循环次数。 - 空间复杂度
O(1): 几个变量使用常数大小的额外空间。