mirror of
https://github.com/krahets/LeetCode-Book.git
synced 2026-01-12 00:19:02 +08:00
4.6 KiB
Executable File
4.6 KiB
Executable File
解题思路:
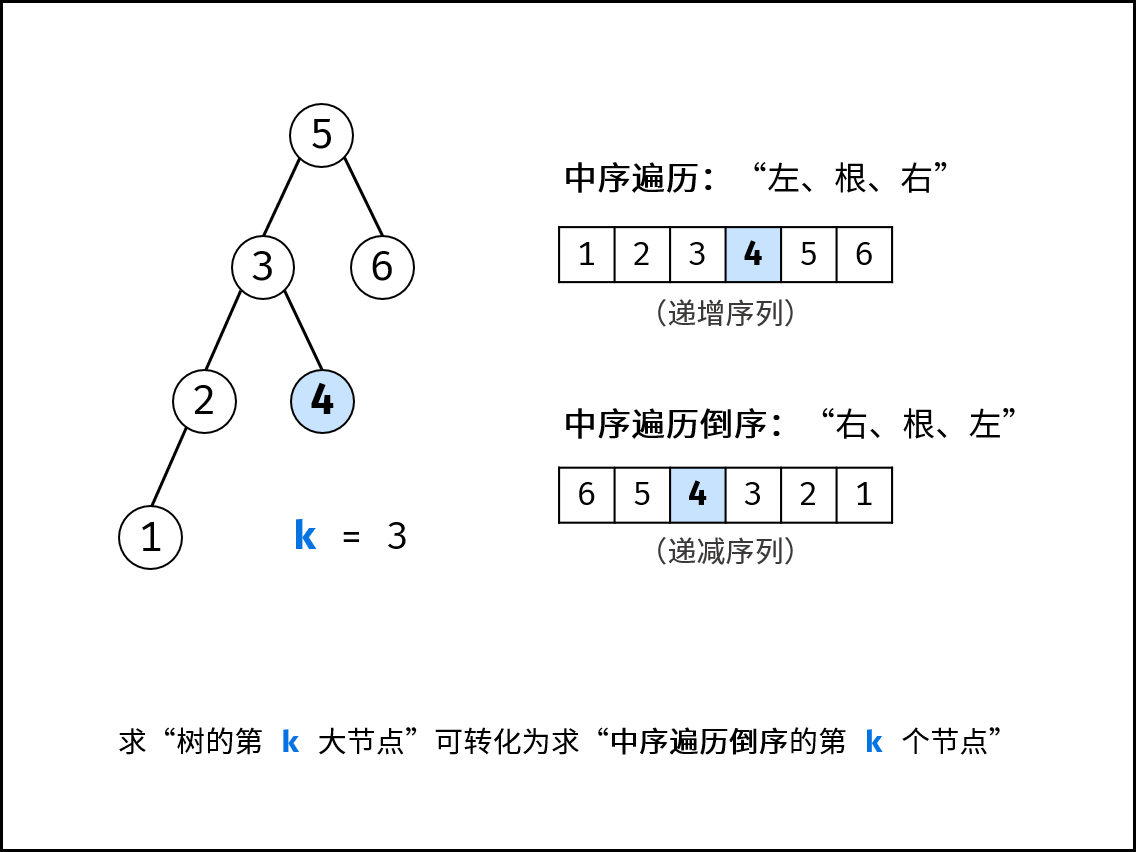
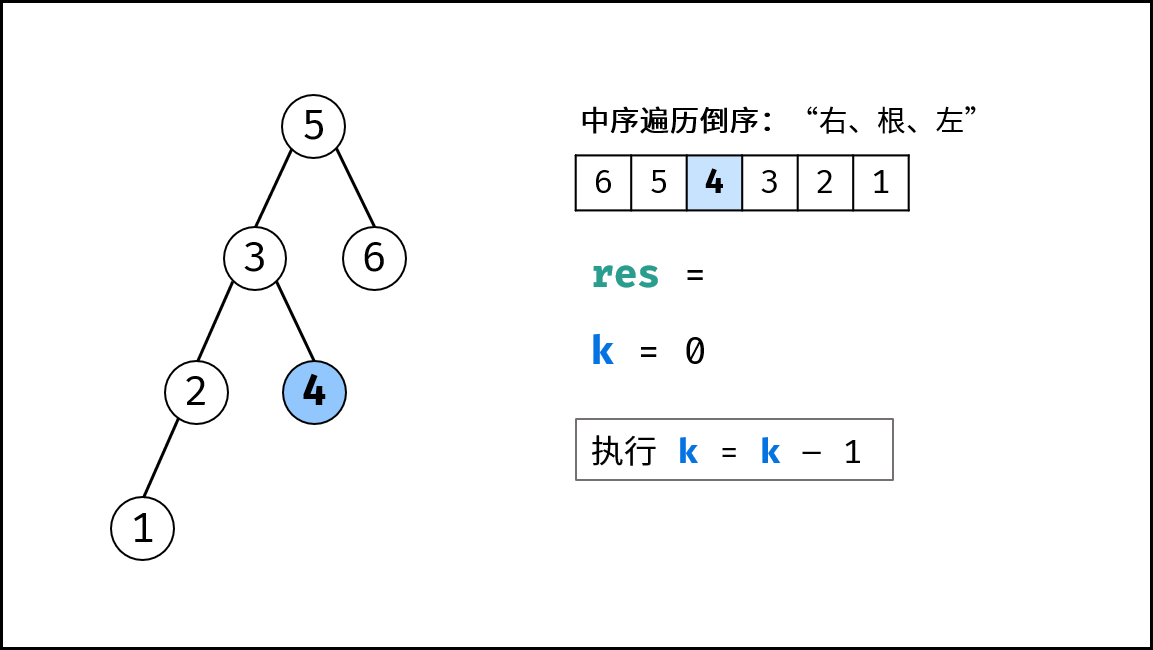
本文解法基于性质:二叉搜索树的中序遍历为递增序列。根据此性质,易得二叉搜索树的 中序遍历倒序 为 递减序列 。
因此,我们可将求 “二叉搜索树第 cnt 大的节点” 可转化为求 “此树的中序遍历倒序的第 cnt 个节点”。
下图中的
k对应本题的cnt。
中序遍历 为 “左、根、右” 顺序,递归代码如下:
# 打印中序遍历
def dfs(root):
if not root: return
dfs(root.left) # 左
print(root.val) # 根
dfs(root.right) # 右
// 打印中序遍历
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return;
dfs(root.left); // 左
System.out.println(root.val); // 根
dfs(root.right); // 右
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return;
dfs(root->left);
cout << root->val;
dfs(root->right);
}
中序遍历的倒序 为 “右、根、左” 顺序,递归法代码如下:
# 打印中序遍历倒序
def dfs(root):
if not root: return
dfs(root.right) # 右
print(root.val) # 根
dfs(root.left) # 左
// 打印中序遍历倒序
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return;
dfs(root.right); // 右
System.out.println(root.val); // 根
dfs(root.left); // 左
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return;
dfs(root->right);
cout << root->val;
dfs(root->left);
}
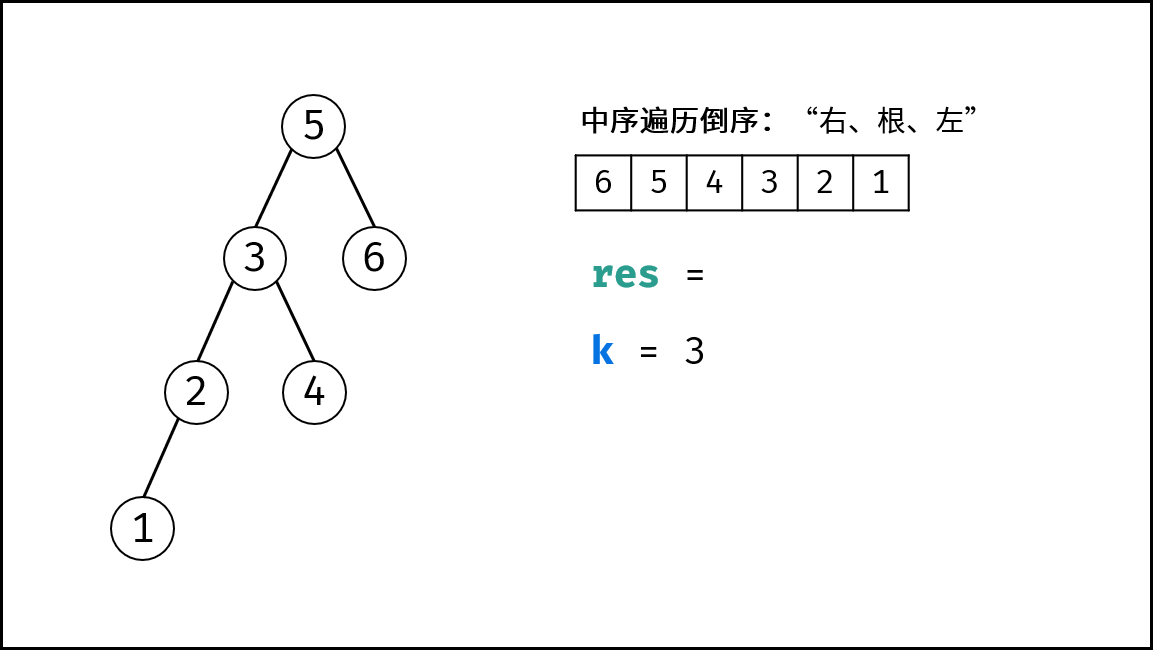
为求第 cnt 个节点,需要实现以下三项工作:
- 递归遍历时计数,统计当前节点的序号;
- 递归到第
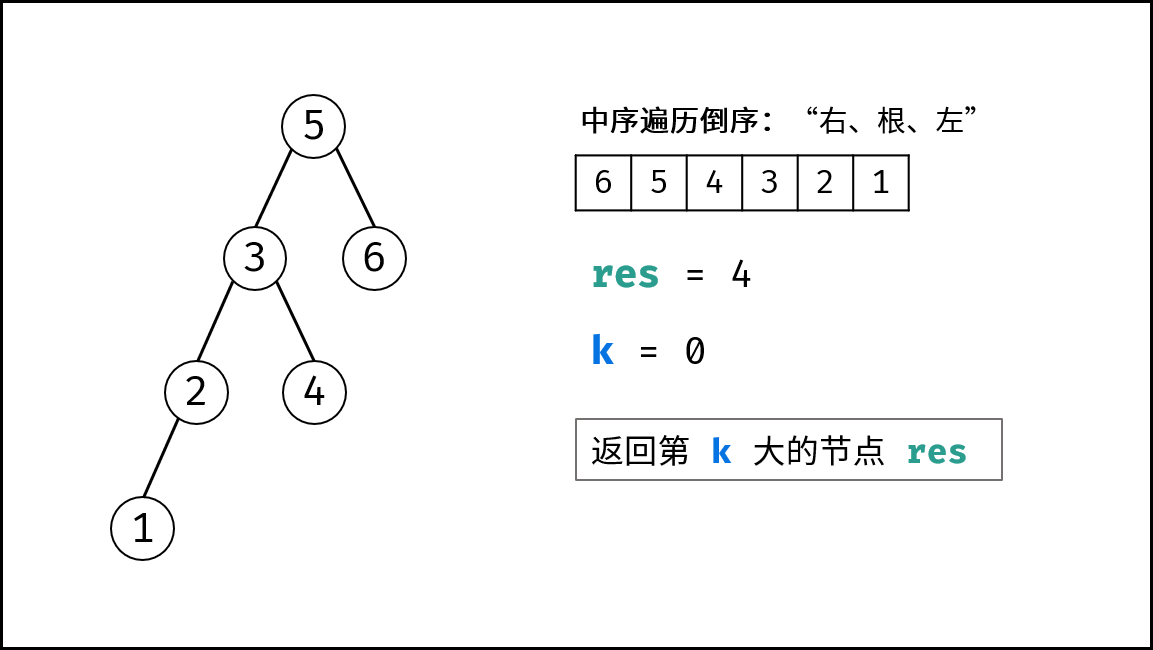
cnt个节点时,应记录结果res; - 记录结果后,后续的遍历即失去意义,应提前终止(即返回);
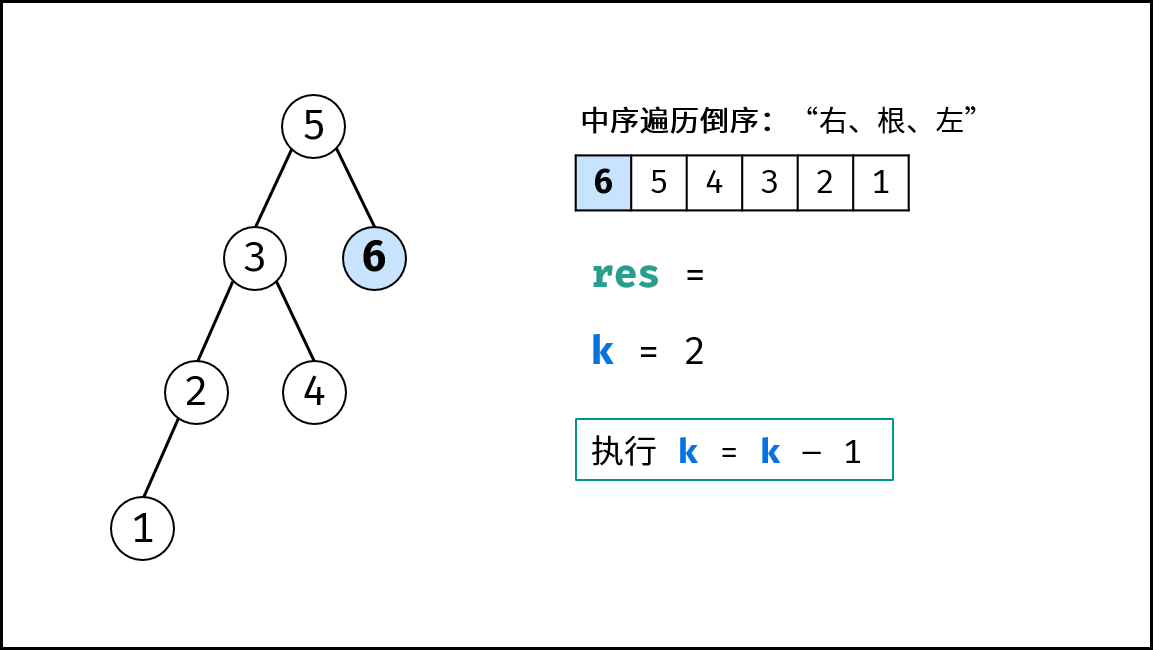
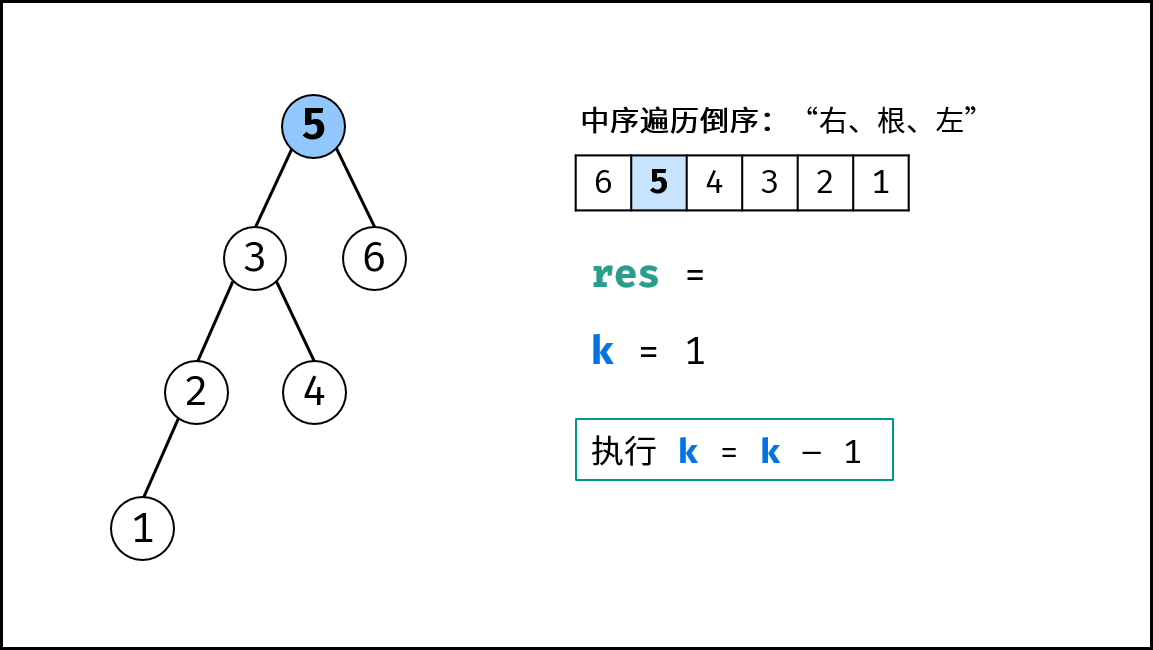
递归解析:
- 终止条件: 当节点
root为空(越过叶节点),则直接返回; - 递归右子树: 即
dfs(root.right); - 递推工作:
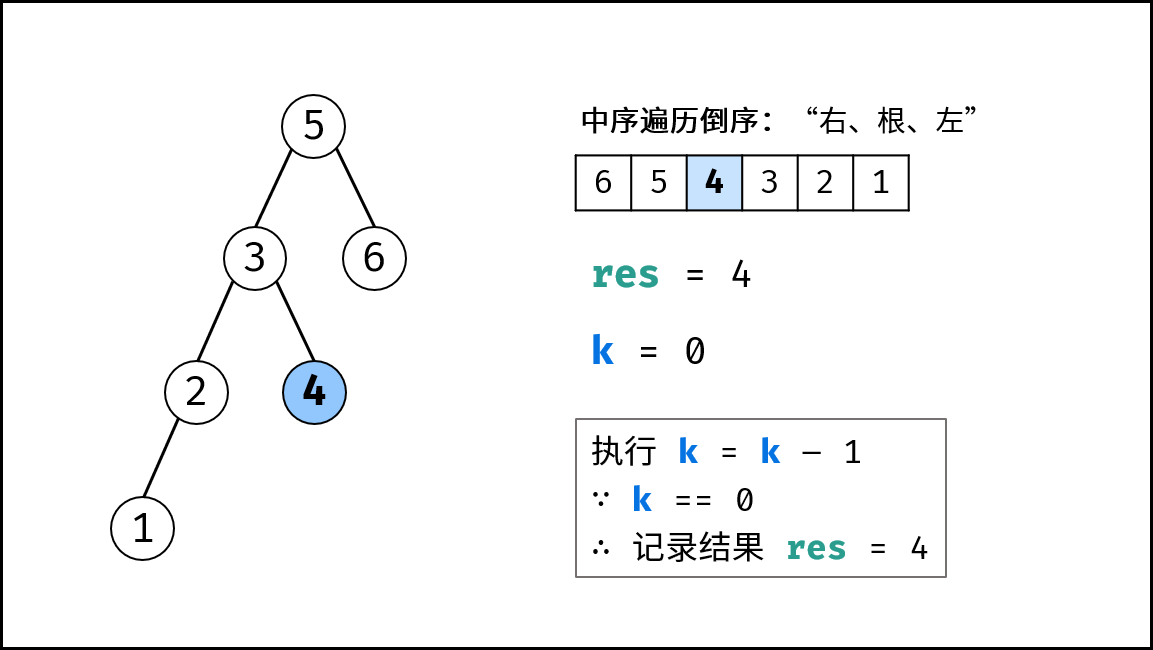
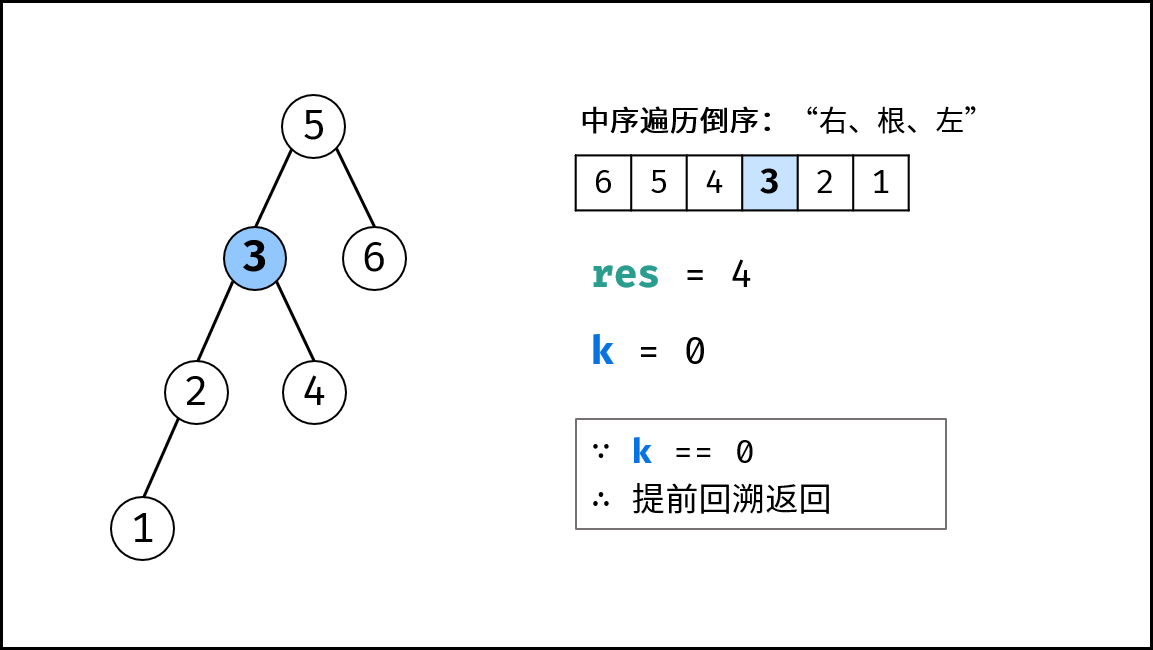
- 提前返回: 若
cnt = 0,代表已找到目标节点,无需继续遍历,因此直接返回; - 统计序号: 执行
cnt = cnt - 1(即从cnt减至0); - 记录结果: 若
cnt = 0,代表当前节点为第cnt大的节点,因此记录res = root.val;
- 提前返回: 若
- 递归左子树: 即
dfs(root.left);
代码:
题目指出:1 \leq cnt \leq N (二叉搜索树节点个数);因此无需考虑 cnt > N 的情况。
若考虑,可以在中序遍历完成后判断 cnt > 0 是否成立,若成立则说明 cnt > N 。
class Solution:
def findTargetNode(self, root: TreeNode, cnt: int) -> int:
def dfs(root):
if not root: return
dfs(root.right)
if self.cnt == 0: return
self.cnt -= 1
if self.cnt == 0: self.res = root.val
dfs(root.left)
self.cnt = cnt
dfs(root)
return self.res
class Solution {
int res, cnt;
public int findTargetNode(TreeNode root, int cnt) {
this.cnt = cnt;
dfs(root);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return;
dfs(root.right);
if(cnt == 0) return;
if(--cnt == 0) res = root.val;
dfs(root.left);
}
}
class Solution {
public:
int findTargetNode(TreeNode* root, int cnt) {
this->cnt = cnt;
dfs(root);
return res;
}
private:
int res, cnt;
void dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return;
dfs(root->right);
if(cnt == 0) return;
if(--cnt == 0) res = root->val;
dfs(root->left);
}
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度
O(N): 当树退化为链表时(全部为右子节点),无论cnt的值大小,递归深度都为N,占用O(N)时间。 - 空间复杂度
O(N): 当树退化为链表时(全部为右子节点),系统使用O(N)大小的栈空间。