7.2 KiB
Executable File
解题思路:
题目要求时间复杂度 O(N) ,空间复杂度 O(1) ,因此首先排除 暴力法 和 哈希表统计法 。
简化问题: 一个整型数组
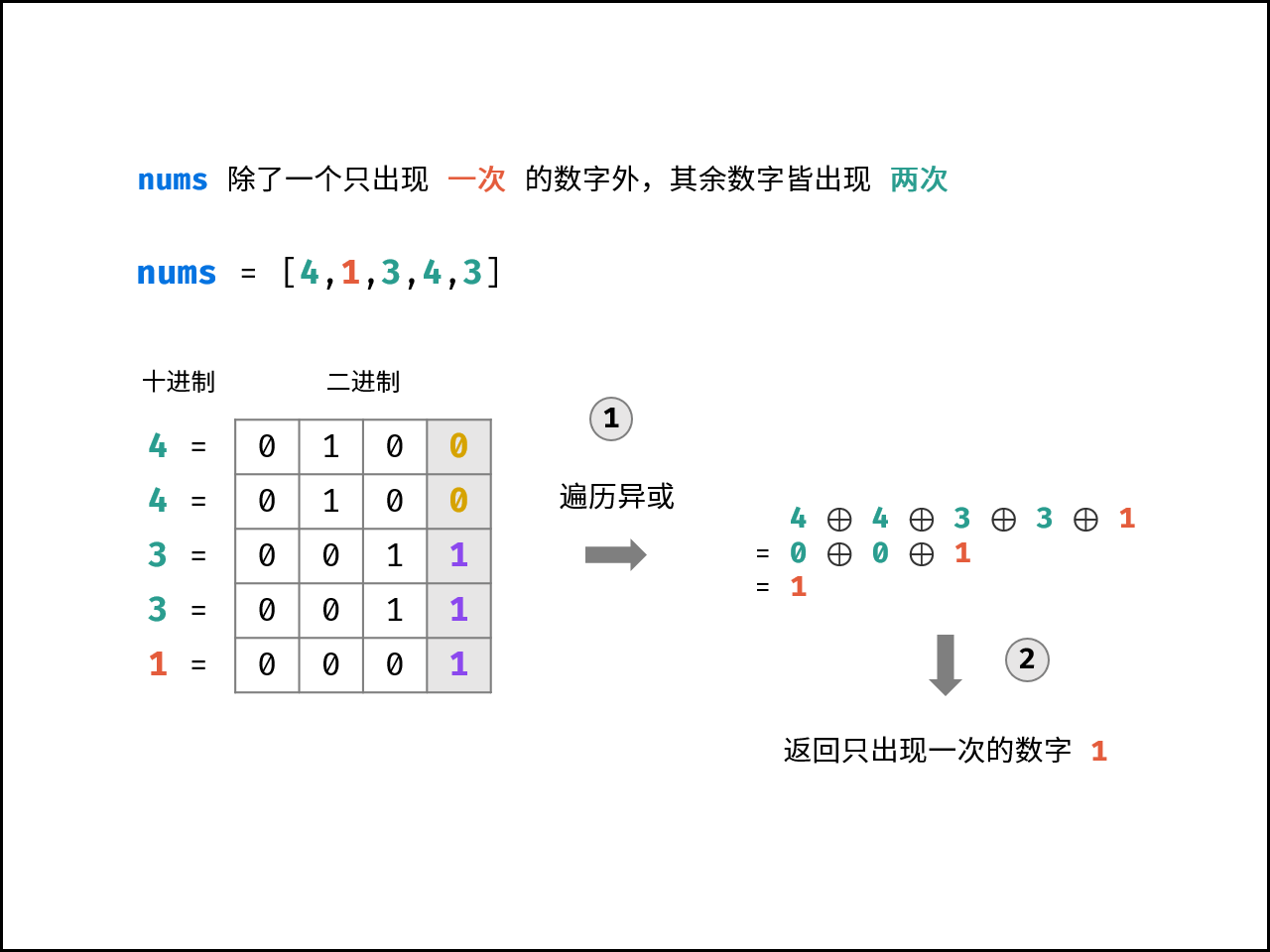
sockets里除 一个 数字之外,其他数字都出现了两次。
设整型数组 sockets 中出现一次的数字为 x ,出现两次的数字为 a, a, b, b, ... ,即:
sockets = [a, a, b, b, ..., x]
异或运算有个重要的性质,两个相同数字异或为 0 ,即对于任意整数 a 有 a \oplus a = 0 。因此,若将 sockets 中所有数字执行异或运算,留下的结果则为 出现一次的数字 $x$ ,即:
\begin{aligned}
& \ \ a \oplus a \oplus b \oplus b \oplus ... \oplus x \\
= & \ \ 0 \oplus 0 \oplus ... \oplus x \\
= & \ \ x
\end{aligned}
异或运算满足交换律 a \oplus b = b \oplus a ,即以上运算结果与 sockets 的元素顺序无关。代码如下:
def singleNumber(self, sockets: List[int]) -> List[int]:
x = 0
for num in sockets: # 1. 遍历 sockets 执行异或运算
x ^= num
return x; # 2. 返回出现一次的数字 x
public int[] singleNumber(int[] sockets) {
int x = 0;
for(int num : sockets) // 1. 遍历 sockets 执行异或运算
x ^= num;
return x; // 2. 返回出现一次的数字 x
}
vector<int> singleNumber(vector<int>& sockets) {
int x = 0;
for(int num : sockets) // 1. 遍历 sockets 执行异或运算
x ^= num;
return x; // 2. 返回出现一次的数字 x
}
下图中的
nums对应本题的sockets。
本题难点: 数组
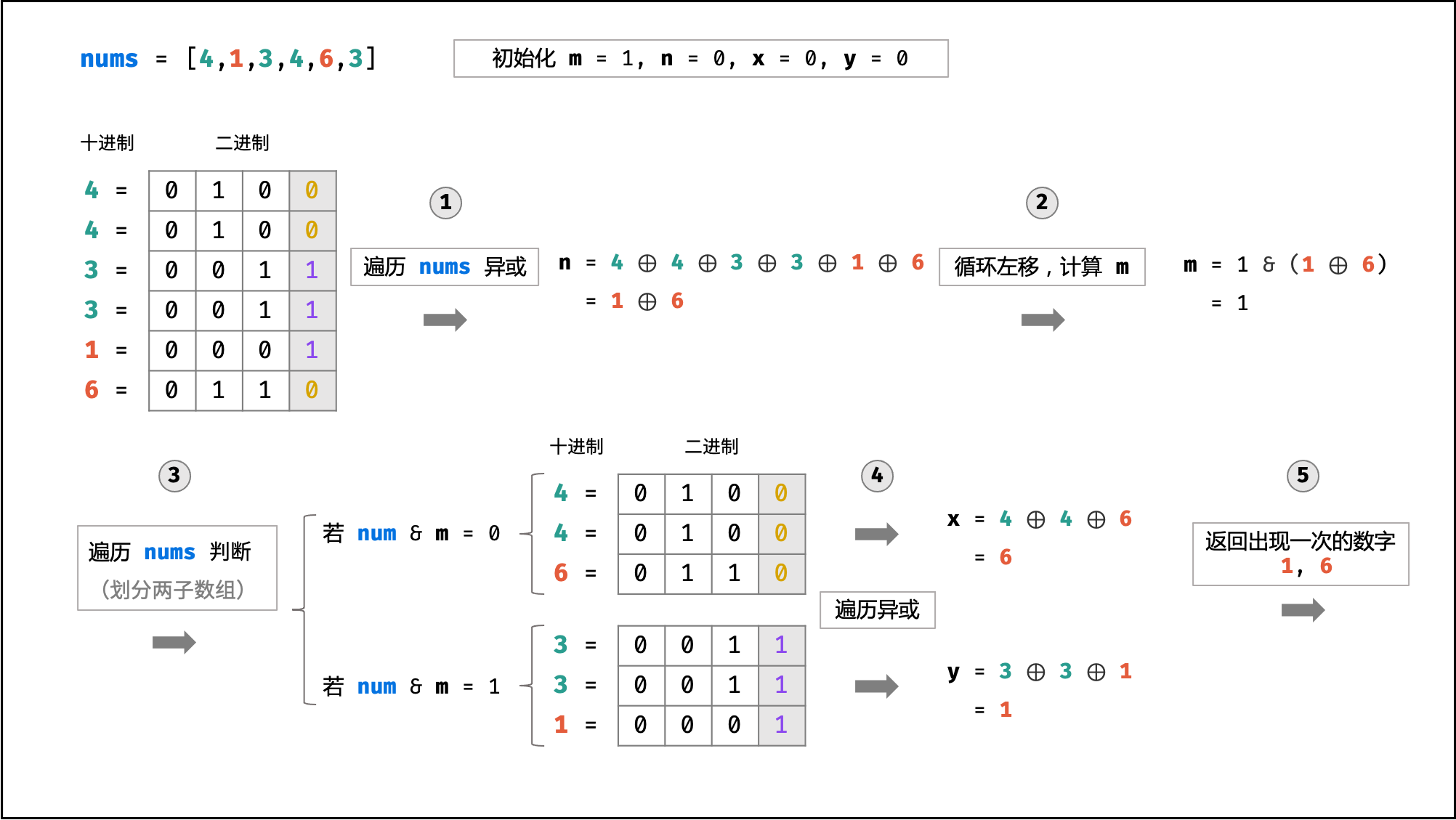
sockets有 两个 只出现一次的数字,因此无法通过异或直接得到这两个数字。
设两个只出现一次的数字为 x , y ,由于 x \ne y ,则 x 和 y 二进制至少有一位不同(即分别为 0 和 1 ),根据此位可以将 sockets 拆分为分别包含 x 和 y 的两个子数组。
易知两子数组都满足 「除一个数字之外,其他数字都出现了两次」。因此,仿照以上简化问题的思路,分别对两子数组遍历执行异或操作,即可得到两个只出现一次的数字 x, y 。
算法流程:
- 遍历
sockets执行异或:
- 设整型数组
sockets = [a, a, b, b, ..., x, y],对sockets中所有数字执行异或,得到的结果为x \oplus y,即:
\begin{aligned}
& \ \ a \oplus a \oplus b \oplus b \oplus ... \oplus x \oplus y \\
= & \ \ 0 \oplus 0 \oplus ... \oplus x \oplus y \\
= & \ \ x \oplus y
\end{aligned}
- 循环左移计算
m:
-
根据异或运算定义,若整数
x \oplus y某二进制位为1,则x和y的此二进制位一定不同。换言之,找到x \oplus y某为1的二进制位,即可将数组sockets拆分为上述的两个子数组。根据与运算特点,可知对于任意整数a有:- 若
a \& 0001 \ne 0,则a的第一位为1; - 若
a \& 0010 \ne 0,则a的第二位为1; - 以此类推……
- 若
-
因此,初始化一个辅助变量
m = 1,通过与运算从右向左循环判断,可 获取整数x \oplus y首位 $1$ ,记录于m中,代码如下:
while z & m == 0: # m 循环左移一位,直到 z & m != 0
m <<= 1
while(z & m == 0) // m 循环左移一位,直到 z & m != 0
m <<= 1
while(z & m == 0) // m 循环左移一位,直到 z & m != 0
m <<= 1
- 拆分
sockets为两个子数组: - 分别遍历两个子数组执行异或:
- 通过遍历判断
sockets中各数字和m做与运算的结果,可将数组拆分为两个子数组,并分别对两个子数组遍历求异或,则可得到两个只出现一次的数字,代码如下:
for num in sockets:
if num & m: x ^= num # 若 num & m != 0 , 划分至子数组 1 ,执行遍历异或
else: y ^= num # 若 num & m == 0 , 划分至子数组 2 ,执行遍历异或
return x, y # 遍历异或完毕,返回只出现一次的数字 x 和 y
for(int num: sockets) {
if((num & m) != 0) x ^= num; // 若 num & m != 0 , 划分至子数组 1 ,执行遍历异或
else y ^= num; // 若 num & m == 0 , 划分至子数组 2 ,执行遍历异或
}
return new int[] {x, y}; // 遍历异或完毕,返回只出现一次的数字 x 和 y
for(int num : sockets) {
if(num & m) x ^= num; // 若 num & m != 0 , 划分至子数组 1 ,执行遍历异或
else y ^= num; // 若 num & m == 0 , 划分至子数组 2 ,执行遍历异或
}
return vector<int> {x, y}; // 遍历异或完毕,返回只出现一次的数字 x 和 y
- 返回值:
- 返回只出现一次的数字 x, y 即可。
下图中的
nums对应本题的sockets。
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度
O(N): 线性遍历sockets使用O(N)时间,遍历x \oplus y二进制位使用O(32) = O(1)时间。 - 空间复杂度
O(1): 辅助变量a,b,x,y使用常数大小额外空间。
代码:
class Solution:
def sockCollocation(self, sockets: List[int]) -> List[int]:
x, y, n, m = 0, 0, 0, 1
for num in sockets: # 1. 遍历异或
n ^= num
while n & m == 0: # 2. 循环左移,计算 m
m <<= 1
for num in sockets: # 3. 遍历 sockets 分组
if num & m: x ^= num # 4. 当 num & m != 0
else: y ^= num # 4. 当 num & m == 0
return x, y # 5. 返回出现一次的数字
class Solution {
public int[] sockCollocation(int[] sockets) {
int x = 0, y = 0, n = 0, m = 1;
for(int num : sockets) // 1. 遍历异或
n ^= num;
while((n & m) == 0) // 2. 循环左移,计算 m
m <<= 1;
for(int num: sockets) { // 3. 遍历 sockets 分组
if((num & m) != 0) x ^= num; // 4. 当 num & m != 0
else y ^= num; // 4. 当 num & m == 0
}
return new int[] {x, y}; // 5. 返回出现一次的数字
}
}
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> sockCollocation(vector<int>& sockets) {
int x = 0, y = 0, n = 0, m = 1;
for(int num : sockets) // 1. 遍历异或
n ^= num;
while((n & m) == 0) // 2. 循环左移,计算 m
m <<= 1;
for(int num : sockets) { // 3. 遍历 sockets 分组
if(num & m) x ^= num; // 4. 当 num & m != 0
else y ^= num; // 4. 当 num & m == 0
}
return vector<int> {x, y}; // 5. 返回出现一次的数字
}
};