mirror of
https://github.com/krahets/LeetCode-Book.git
synced 2026-01-12 00:19:02 +08:00
4.9 KiB
Executable File
4.9 KiB
Executable File
解题思路:
本题在简单问题上做了许多限制,需要使用排除法一步步导向答案。
1+2+...+(target-1)+target 的计算方法主要有三种:平均计算、迭代、递归。
方法一: 平均计算 问题: 此计算必须使用 乘除法 ,因此本方法不可取,直接排除。
public int mechanicalAccumulator(int target) {
return (1 + target) * target / 2;
}
def mechanicalAccumulator(target):
return (1 + target) * target // 2
int mechanicalAccumulator(int target) {
return (1 + target) * target / 2;
}
方法二: 迭代
问题: 循环必须使用 while 或 for ,因此本方法不可取,直接排除。
public int mechanicalAccumulator(int target) {
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= target; i++)
res += i;
return res;
}
def mechanicalAccumulator(target):
res = 0
for i in range(1, target + 1):
res += i
return res
int mechanicalAccumulator(int target) {
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= target; i++)
res += i;
return res;
}
方法三: 递归
问题: 终止条件需要使用 if ,因此本方法不可取。
思考: 除了 if 和 switch 等判断语句外,是否有其他方法可用来终止递归?
public int mechanicalAccumulator(int target) {
if(target == 1) return 1;
target += mechanicalAccumulator(target - 1);
return target;
}
def mechanicalAccumulator(target):
if target == 1: return 1
target += mechanicalAccumulator(target - 1)
return target
int mechanicalAccumulator(int target) {
if(target == 1) return 1;
target += mechanicalAccumulator(target - 1);
return target;
}
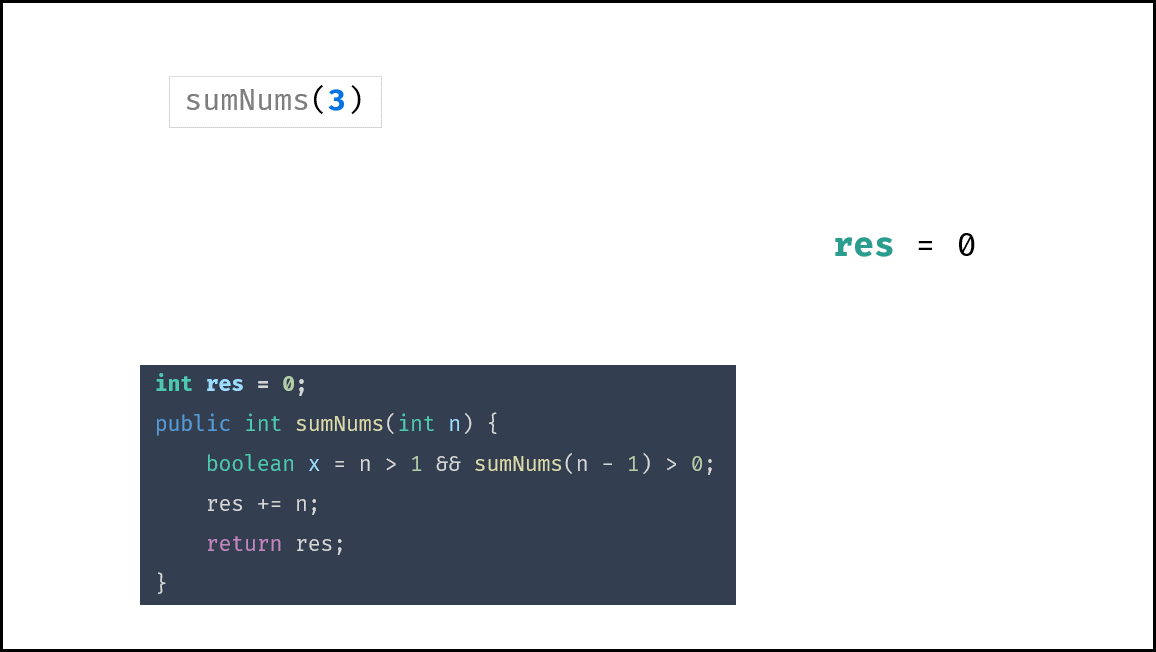
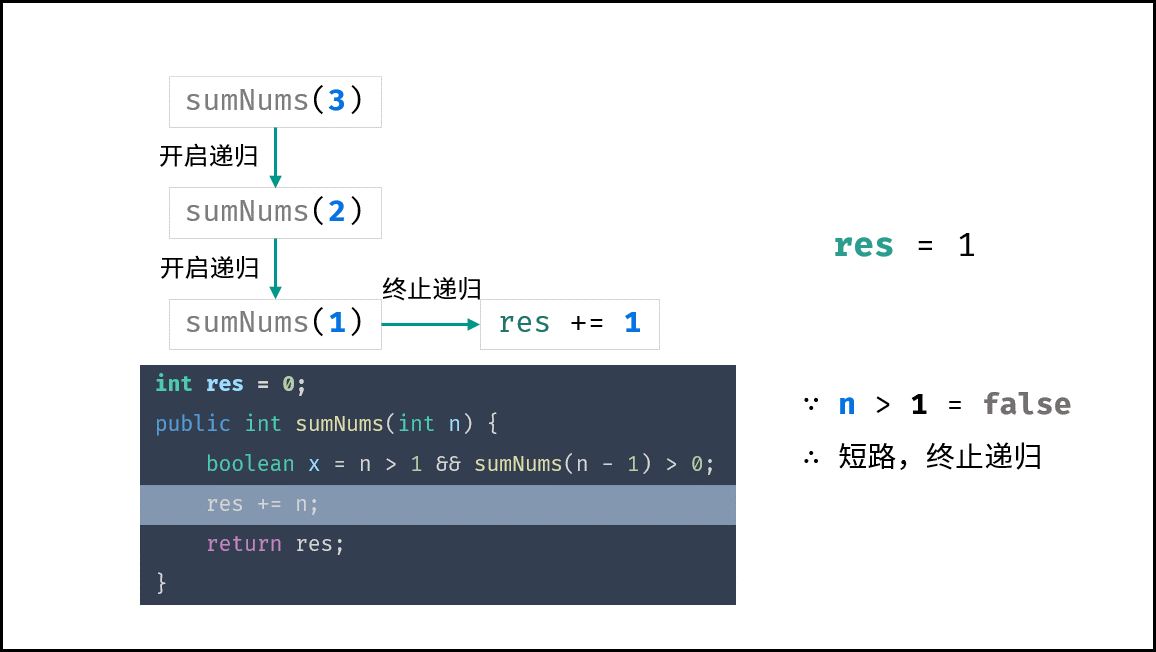
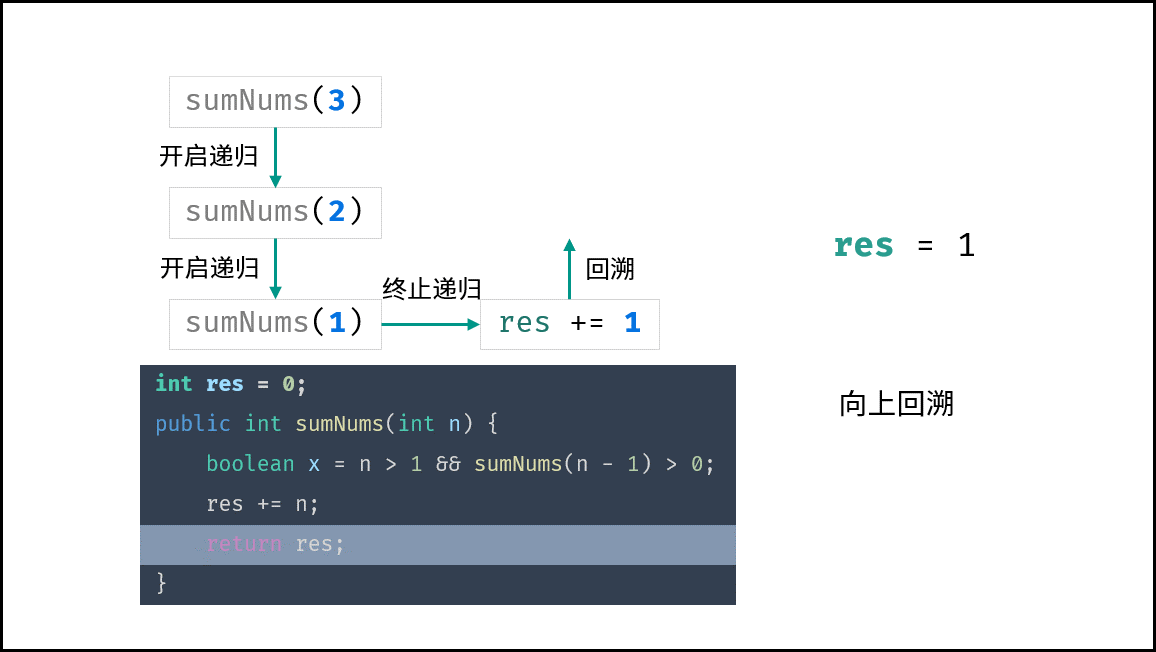
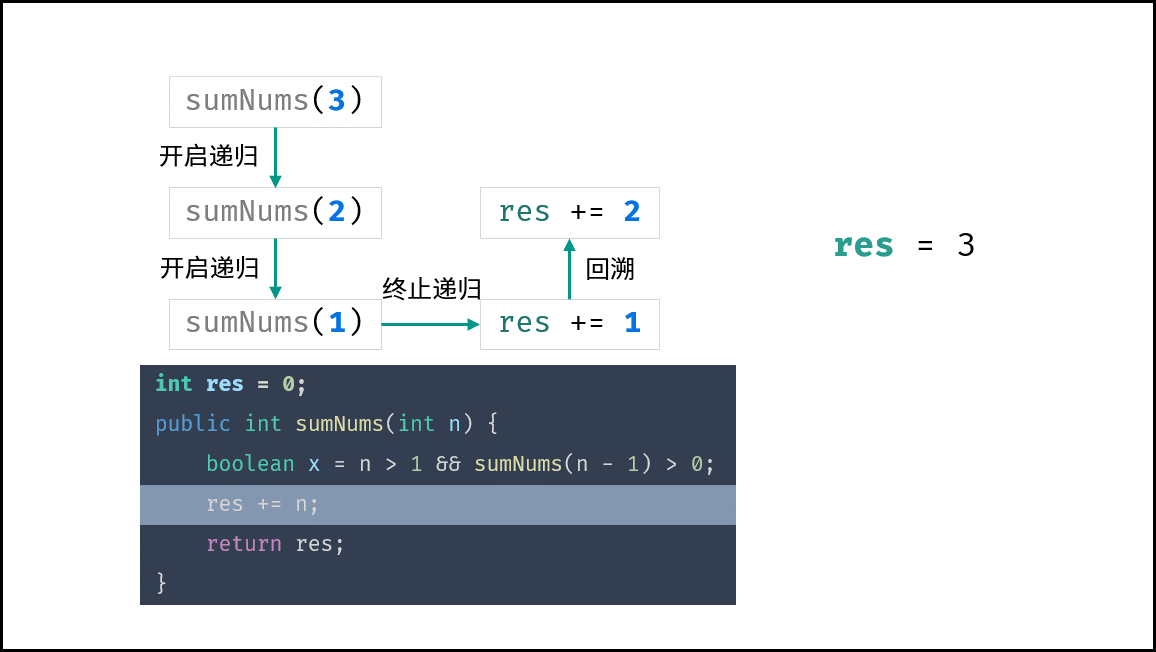
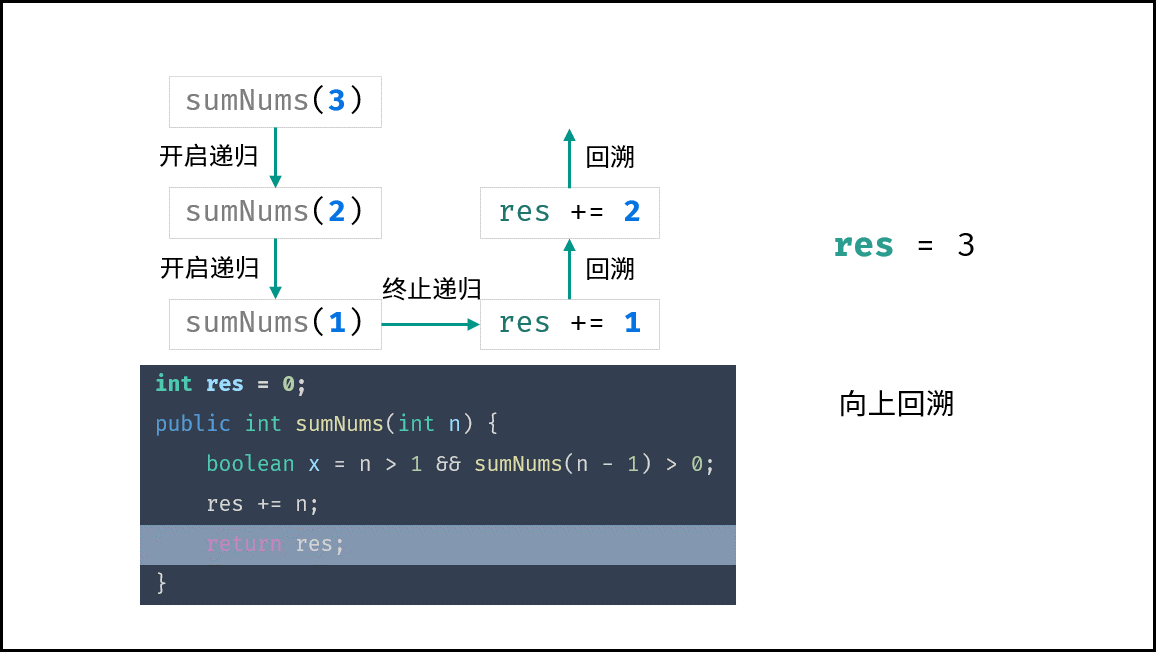
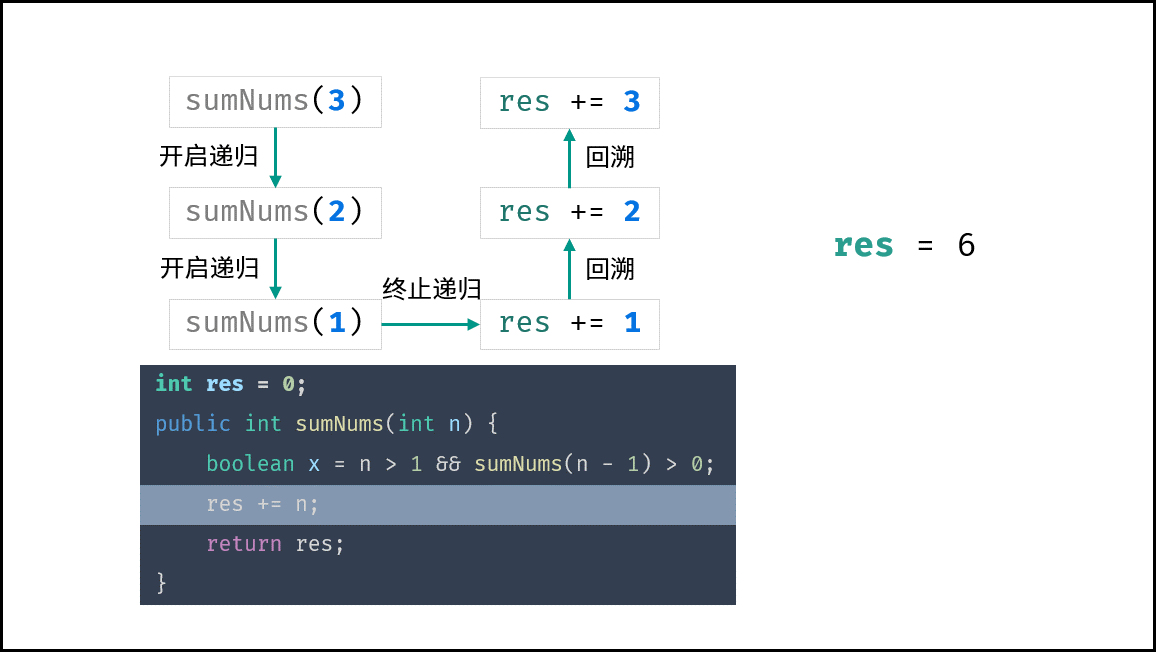
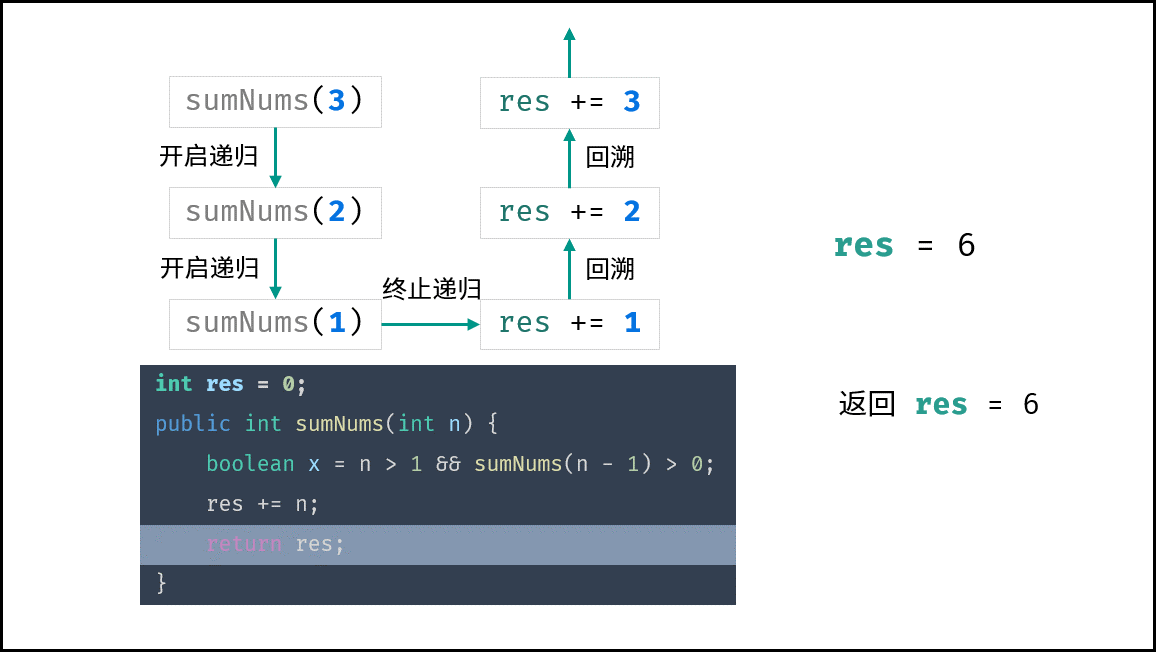
下图中的
sumNums()对应本题的mechanicalAccumulator。
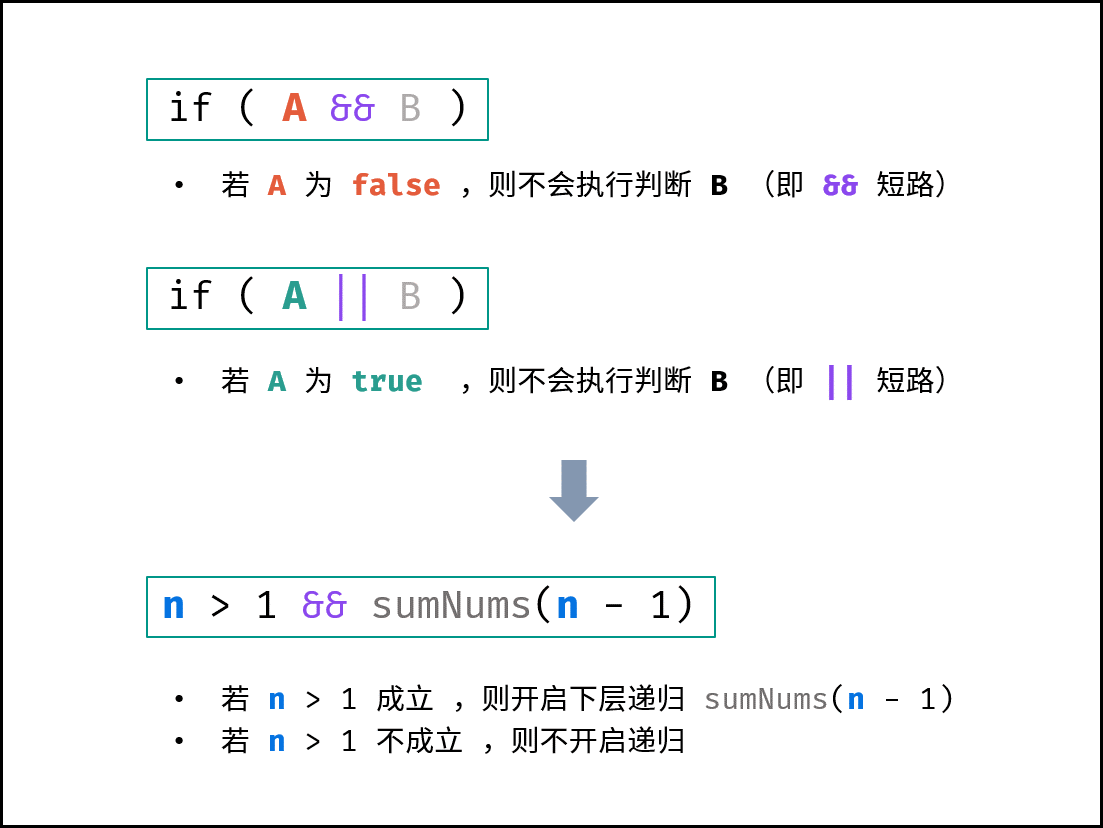
逻辑运算符的短路效应:
常见的逻辑运算符有三种,即 “与 \&\& ”,“或 || ”,“非 ! ” ;而其有重要的短路效应,如下所示:
if(A && B) // 若 A 为 false ,则 B 的判断不会执行(即短路),直接判定 A && B 为 false
if(A || B) // 若 A 为 true ,则 B 的判断不会执行(即短路),直接判定 A || B 为 true
本题需要实现 “当 target = 1 时终止递归” 的需求,可通过短路效应实现。
target > 1 && mechanicalAccumulator(target - 1) // 当 target = 1 时 target > 1 不成立 ,此时 “短路” ,终止后续递归
代码:
- Java 中,为构成语句,需加一个辅助布尔量
x,否则会报错; - Java 中,开启递归函数需改写为
mechanicalAccumulator(target - 1) > 0,此整体作为一个布尔量输出,否则会报错; - 初始化变量
res记录结果。( Java 可使用第二栏的简洁写法,不用借助变量res)。
class Solution {
int res = 0;
public int mechanicalAccumulator(int target) {
boolean x = target > 1 && mechanicalAccumulator(target - 1) > 0;
res += target;
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
public int mechanicalAccumulator(int target) {
boolean x = target > 1 && (target += mechanicalAccumulator(target - 1)) > 0;
return target;
}
}
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.res = 0
def mechanicalAccumulator(self, target: int) -> int:
target > 1 and self.mechanicalAccumulator(target - 1)
self.res += target
return self.res
class Solution {
public:
int mechanicalAccumulator(int target) {
target > 1 && (target += mechanicalAccumulator(target - 1));
return target;
}
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度
O(target): 计算target + (target-1) + ... + 2 + 1需要开启target个递归函数。 - 空间复杂度
O(target): 递归深度达到target,系统使用O(target)大小的额外空间。